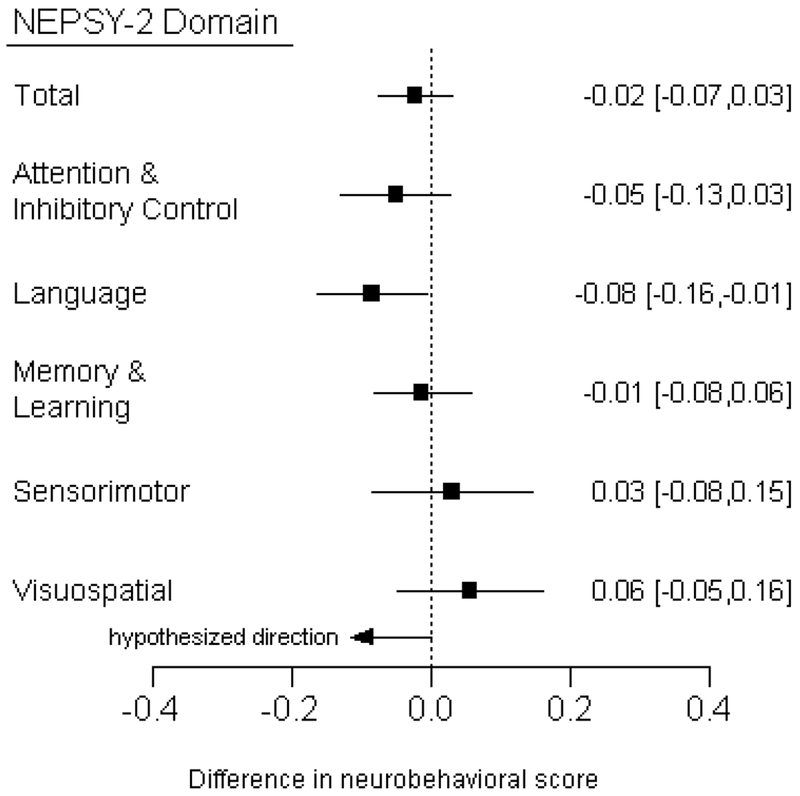
Figure 1.
Difference [95% confidence interval] in neurobehavioral scores associated with living 100m closer to the edge of the nearest floricultural crop. Linear regression models were adjusted for age, sex, race, height-for-age z-score, hemoglobin, maternal education, and cohabitation with a flower plantation worker. We hypothesized that children residing closer to greenhouse agriculture had greater odds of having low neurobehavioral scores.