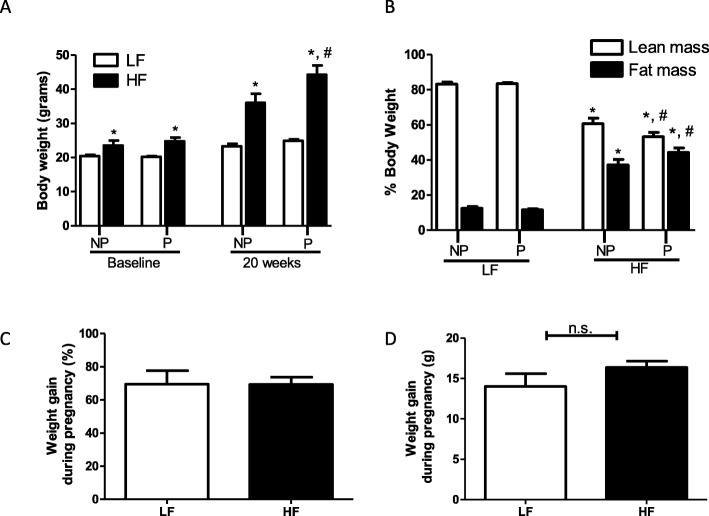
Fig. 1.
Weight gain with high-fat feeding is exacerbated after pregnancy. a Body weight of low-fat (LF)– and high-fat (HF)–fed mice at baseline (4 weeks of diet feeding, prior to pregnancy) and after 20 weeks of diet feeding in nulliparous (NP) and postpartum (P) female mice (mean of 10.5 weeks after delivery). b Lean and fat mass (as percentage of body weight) of LF- and HF-fed mice after 20 weeks of diet feeding in NP and P female mice (mean of 10.5 weeks after delivery). c Percent weight gain and (d) grams gained during pregnancy in LF- and HF-fed mice. Data are mean + SEM from n = 9–11 mice per group. *P < 0.01 compared with LF within group using 2-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak pairwise analysis; #P < 0.05 compared with NP within diet group using 2-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak pairwise analysis