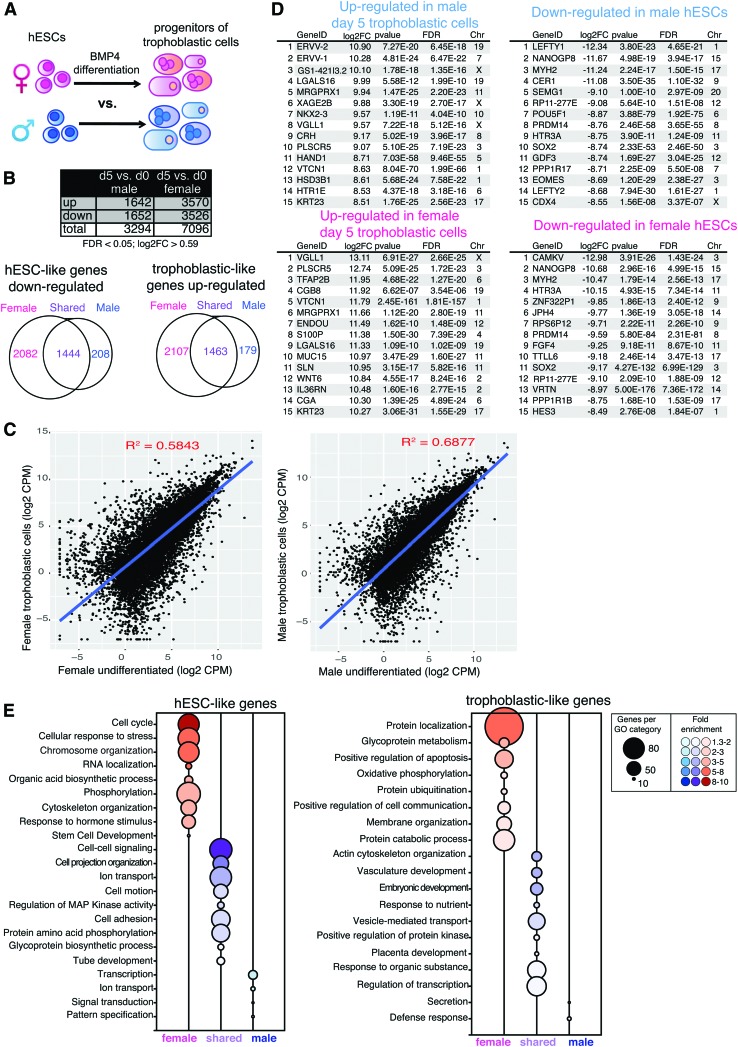
FIG. 5.
Female-biased sex differences with in vitro differentiation of hESCs to trophoblastic cells. (A) Schematic showing the comparison of female BMP4/A/P differentiation (pink) with male BMP4/A/P differentiation (blue). Cells were differentiated for 5 days. (B) Top: table showing significant DEGs for female and male cells during trophoblastic differentiation (FDR <0.05, log2FC >0.59). Bottom: Venn diagrams of downregulated (left, hESC) and upregulated (right, trophoblastic cells) genes during the differentiation of trophoblastic progenitor cells in male and female cells. Numbers of genes unique to females (pink), genes unique to males (blue), and genes in shared in both males and females (purple) are shown. (C) Scatterplots (Log2 CPMs) of genes over-represented in hESCs compared with progenitors of trophoblastic cells (females, left; males, right). (D) Top: lists of the top 15 genes differentially expressed during the generation of trophoblastic progenitors (upregulated, left) from hESCs (downregulated, right) in male cells. Bottom: lists of the top 15 genes differentially expressed during the generation of trophoblastic progenitors (upregulated, left) from hESCs (downregulated, right) in female cells. (E) GO enrichment of genes significantly downregulated (left, hESCs) and upregulated (right, trophoblastic cells) during the differentiation of trophoblastic progenitor cells (GO BP “fat” terms, enrichment score ≥1.3; P < 0.05). GO, Gene Ontology. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/scd