Figure 7.
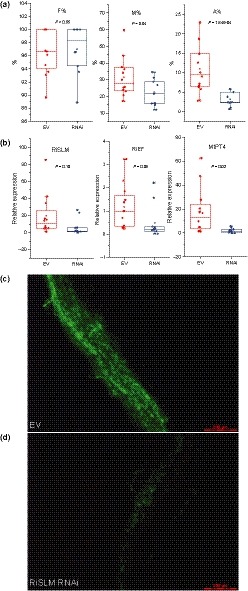
Host‐induced gene silencing of RiSLM) reduces mycorrhization in Medicago truncatula. (a) Frequency (F%) remains the same, whereas mycorrhization intensity in the root (M%) and arbuscule abundance in the root (A%) are reduced in RiSLM‐silenced roots. For the empty vector control (EV), 12 biological replicates were used. For RiSLM RNA interference (RNAi), 10 biological replicates were used. (b) Quantitative PCR analysis of control and RNAi roots showing RiSLM expression level relative to Rhizophagus irregularis elongation factor 1α (RiEF) and MtPT4 expression levels relative to Medicago elongation factor 1α (MtEF). Successful silencing of RiSLM (relative to RiEF) reduces RiEF and MtPT4 expression (relative to MtEF), indicating reduced mycorrhization and arbuscule abundance. Twelve replicates (individual transgenic roots) were used for EV. Eleven replicates were used for RNAi. Student’s t‐test P‐values are indicated for (a) and (b). For all box plots, boxes represent interquartile range (IQR) and whiskers represent 1.5IQR. (c, d) Wheat germ agglutinin‐Alexa Fluor 488 staining of mycorrhization in (d) RiSLM‐silenced roots and (c) control roots (c). Bars, 200 µm.
