Figure 1.
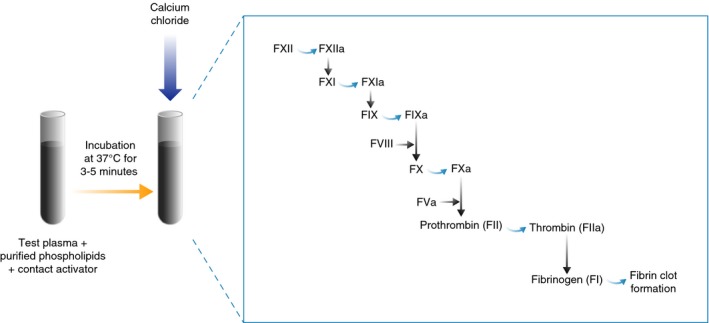
Schematic of the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) method. Contact activator (glass, silica, kaolin, celite, ellagic acid or sulfatides) and phospholipid (derived from soybean, rabbit or bovine brain, human placenta or of synthetic origin) are added to the test plasma and incubated at 37°C to allow the activation of the contact system. Calcium is then added to initiate the activation of the intrinsic and common pathways and, ultimately, fibrin clot formation. The aPTT is quantified as the time (seconds) taken for the clot to form from the time point at which calcium is added and is dependent on all of the intrinsic pathway factors, including factor (F) VIII, present in the test plasma (with the exception of FII). A burst of thrombin formation occurs after sufficient levels of activated FVIII (FVIIIa) have been generated through feedback activation by thrombin, leading to the formation of a clot.5 Adapted with permission from Adcock et al72
