Figure 5.
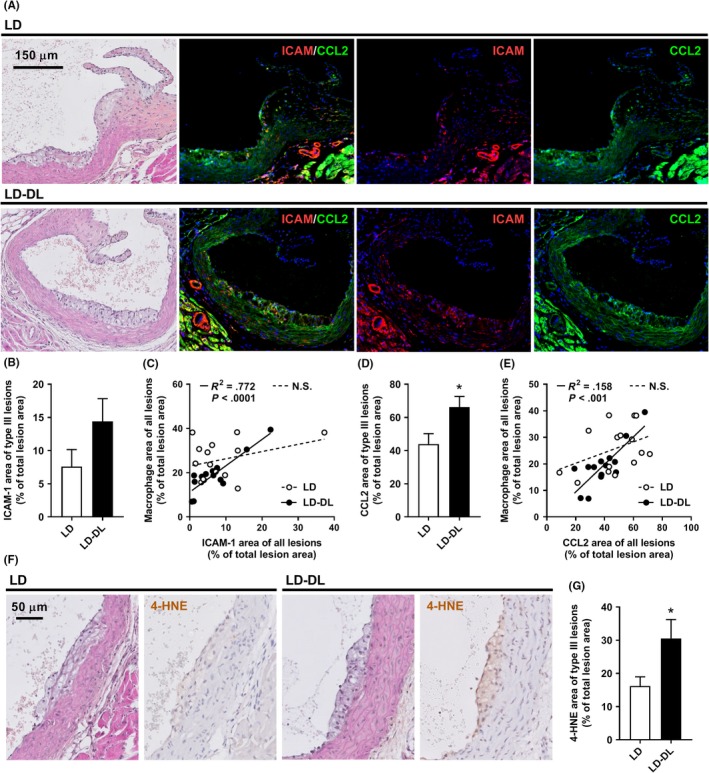
Weekly alternating light‐dark cycles increase CCL2 expression within atherosclerotic lesions. APOE*3‐Leiden.CETP mice were exposed to either regular light‐dark cycles (LD) or weekly alternating light‐dark cycles (12 h shifts; LD‐DL) (n = 15/group) for 15 wk, after which mice were sacrificed, hearts were isolated, and a double‐staining of ICAM‐1 and CCL2 was performed on sections of the aortic root. (A) Representative pictures show lesion areas in LD and LD‐DL mice stained with hematoxylin‐phloxine‐saffron (HPS) and double‐stained for ICAM‐1 and CCL2 (stained red and green, respectively) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). (B) ICAM‐1 area was determined within type III lesions, (C) and the relationship between ICAM‐1 and macrophage area was evaluated by Pearson correlation analysis. (D) CCL2 area was also determined within type III lesions and (E) correlated to macrophage area. Solid lines in the correlation plots indicate correlations within the LD‐DL group, and dashed lines indicate correlations within the LD group. (F) Representative pictures showing lesion areas in LD and LD‐DL mice stained with HPS and stained for 4‐hydroxynonenal (4‐HNE) and counterstained with hematoxylin. (G) 4‐HNE area was determined within type III lesions. NS, nonsignificant. Data represent means ± SEM. *P < .05 compared with the LD control group, according to the two‐tailed unpaired Student's t test
