Figure 1.
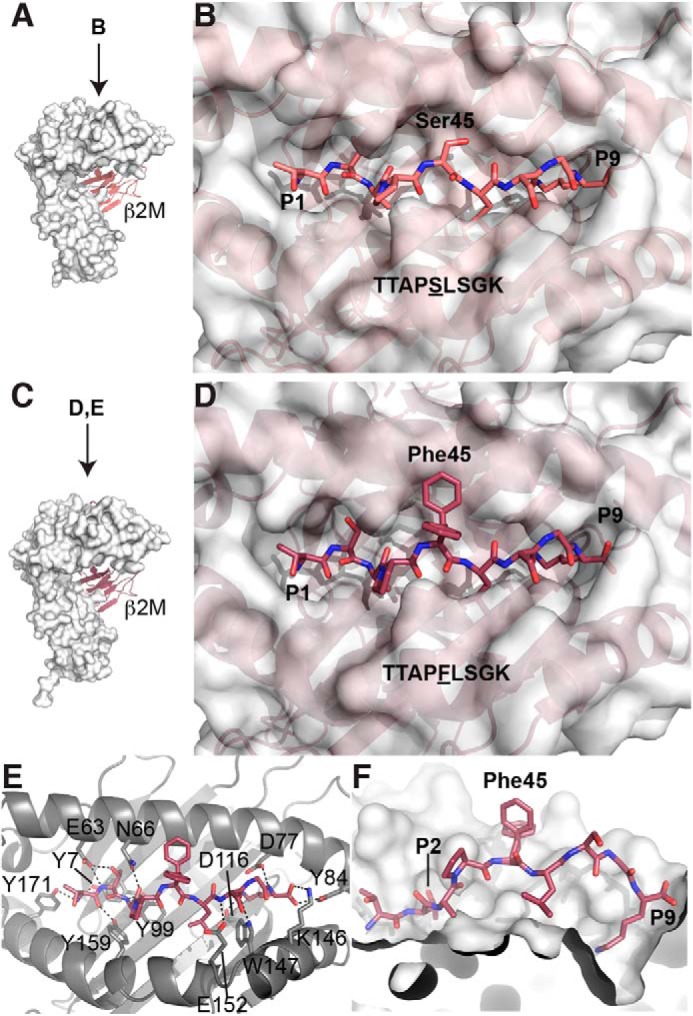
WT and S45F mutant β-catenin peptides bind HLA-A*03:01 with S45F exposed. A, overall structure of HLA-A3 bound to the WT β-catenin peptide (residues 41–49) (PDB entry 6O9B). The HLA-A3 complex is formed as a heterodimer between the heavy chain, represented as a white surface, and β2-microglobulin (β2m), represented as a cartoon. In this orientation, the peptide (not visible) binds in a cleft at the top of the heavy chain from left to right. B, bird's eye view of the WT peptide bound to HLA-A3. The peptide binds in a cleft between the α1 and α2 helices of HLA-A3. The amino acid residues are defined as P1–P9; the residue of interest, β-catenin Ser-45, is in the P5 position and is accessible for binding by an antibody. C, the overall structure of HLA-A3 bound to the S45F mutant β-catenin peptide (residues 41–49) (PDB entry 6O9C), in the same orientation as the WT structure in A. The heavy chain is represented by a white surface, and β2-microglobulin is shown in a cartoon. D, bird's eye view of the mutant peptide bound to HLA-A3. The surface of HLA-A3 is shown. E, detailed interactions of the mutant peptide with HLA-A3. The peptide and the relevant side chains of interacting residues are represented as sticks. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. The peptide is anchored by multiple hydrogen bonds on either end. Two conformations of the mutant β-catenin residue of interest, Phe-45, are shown. F, cut-away view of the peptide-binding cleft. The α2 helix has been removed so that the inner surface of the binding cleft is visible. The anchoring pockets for the residues at P2 and P9 are marked. The two conformations of Phe-45 are shown.
