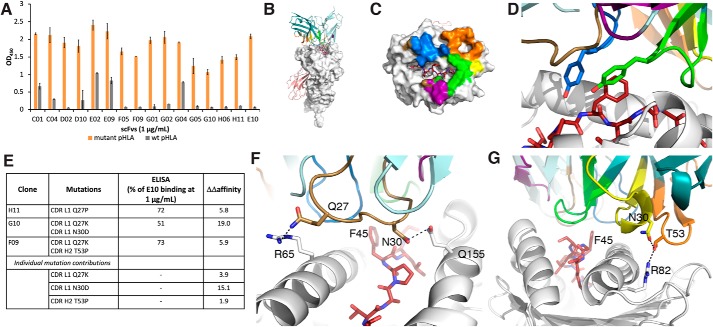
Figure 5.
Development of a model of E10 binding to mutant β-catenin41–49-HLA-A*03:01. A, ELISA of affinity-matured clones. B, model of E10 binding to S45F β-catenin41–49-HLA-A*03:01. HLA-A3 is shown as a white surface. β2-Microglobulin is shown as a salmon cartoon. The light chain of the scFvs is colored in light teal, and the heavy chain in dark teal, with the CDR loops colored as follows: L1 (brown), L2 (purple), L3 (blue), H1 (yellow), H2 (orange), and H3 (green). The mutant peptide is shown as red sticks throughout. C, E10 buries 2,113 Å2 of surface area. The contact surface on HLA-A3 for each of the CDRs has been colored accordingly. D, Phe-45 is recognized by tyrosine residues on CDR L3 and H3. E, table of single and double mutants from affinity maturation studies. Experimental differences in binding and calculated ΔΔaffinity values are compared. F, CDR L1 residues Gln-27 and Asn-30 make hydrogen-bond interactions with HLA-A3 residues Arg-65 and Gln-155, respectively. These interactions would be disrupted upon mutation to proline or lysine. G, CDR H2 residue Thr-53 forms a hydrogen bond with Arg-82 on the HLA, along with a stabilizing interaction with Asn-30 on loop H1. These interactions would be disrupted upon mutation to proline. Error bars, S.D.