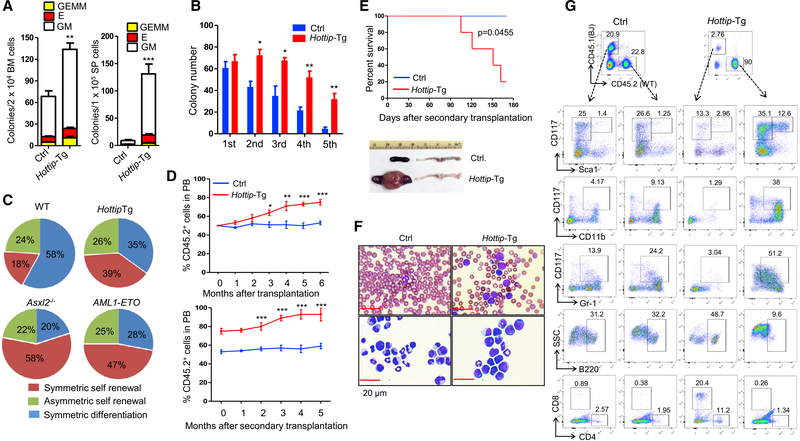
Figure 7. Hottip Transgenic Expression Perturbs HSC Function, Leading to AML-like Disease.
(A) Frequencies of CFU-Cs in the BM and spleen cells from WT and Hottip-Tg mice. GM, granulocytes/macrophages; BFU-E, burst-forming unit-erythrocytes; GEMM, granulocytes/erythrocytes/monocytes/megakaryocytes.
(B) Frequencies of colonies per 100 LSK cells in WT and Hottip-Tg BM cells are shown (1st). Colonies were replated every 7 days for four times (2nd-5th).
(C) Paired-daughter cell assays were performed on CD34− LSK cells from WT, Hottip-Tg mice, Asxl2−/− mice, and AML-ETO mice.
(D) FACS analyses of CD45.2 (donor) chimerisms in the PB of recipients (CD45.1) receiving WT or Hottip-Tg BM cells in first transplantation (top) and second transplantation (bottom).
(E) Kaplan-Meier curve of second transplantation receiving WT (n = 5) and Hottip-Tg (n = 5) BM cells (top) and appearance of spleens and femur of representative WT and moribund Hottip-Tg mice receiving second transplantation (bottom).
(F) Images of PB smears (top) and BM cytospins (bottom) prepared from representative WT and moribund Hottip-Tg mice receiving second transplantation. Scale bar, 20 μm.
(G) FACS analyses showing CD45.2 versus CD45.1 chimerism as well as their respective lineage distribution and LSK/LK cell populations (within Lin− cells) in the BM of representative WT or Hottip-Tg mice receiving second transplantation.
Data in (A), (B), and (D) are presented as mean ± SD; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 by Student’s t test. See also Figure S7.