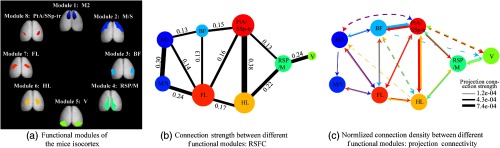
Fig. 8.
Relationship between resting-state connectivity of Vglut2-GCamp6s mice and the axonal projection connectivity. (a) DCBFC was used to cluster mice data, and the two hemispherically symmetric functional modules were combined to form eight functional modules for analysis (M2, secondary motor cortex; M/S, motor areas and somatosensory areas; BF, barrel field cortex; RSP/M, retrosplenial area and motor cortex; V, visual area; HL, hindlimb region; FL, forelimb region; PtA/SSp-tr, parietal association areas and primary somatosensory trunk area). (b) The connection strength (undirected) between different isocortical functional modules. Note that this shows only significant connections (-test, FDR correction, ). The value on the link denotes the ACS between two modules. (c) A corresponding projection (directed) connectivity derived from the voxel-scale model shows only the connections with a normalized connection density greater than . The color of the projection arrow is the same as the injection site. Dashed lines indicate the additional connections of the voxel-scale model that are different from DCBFC.