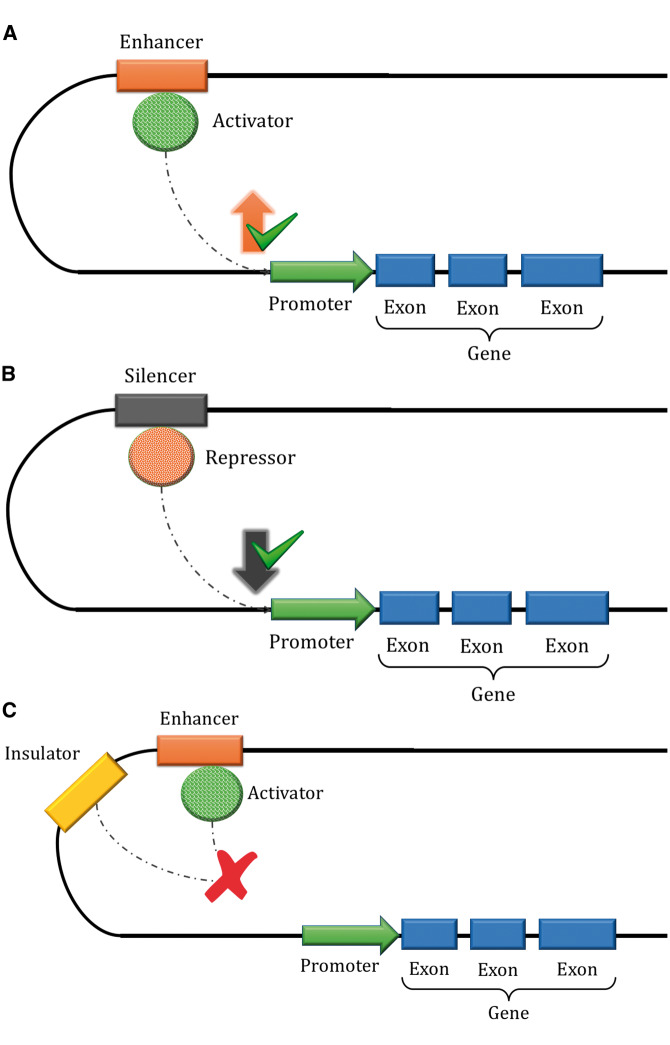
Figure 2.
Representation of the effects of cis-regulatory elements: enhancers (A), silencers (B) and insulators (C). In 2A, the enhancer region binds to a protein (activator) that joins to a specific transcription factor binding site (TFBS) in the promoter region, upregulating the target gene. In 2B, the silencer region binds to another protein (repressor) that binds to a specific TFBS in the promoter region, leading to reduced gene expression. Finally, in 2C, the insulator region interacts with the activator protein of an enhancer, blocking its binding to the promoter and inhibiting gene expression. These interactions are highly controlled and dynamic, and modifications to these elements can dysregulate expression and lead to disease.