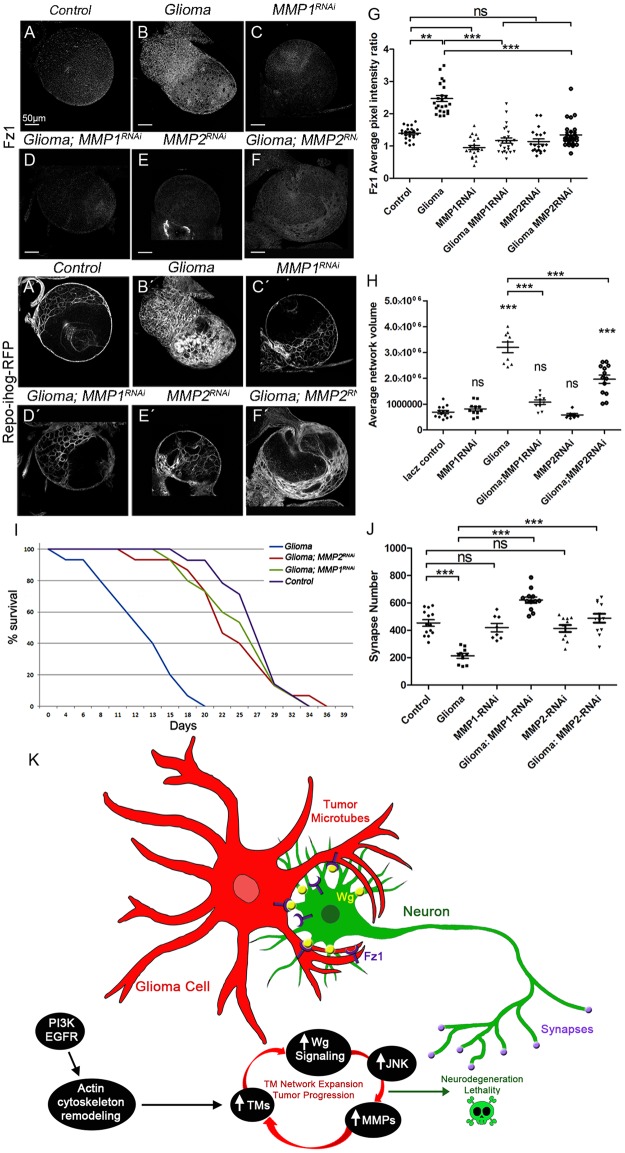
Fig 10. TM expansion and synapse loss in the neurons requires MMPs in glioma.
Brains from third instar larvae displayed at the same scale. Glia are labeled with UAS-Ihog-RFP (gray) driven by repo-Gal4 to visualize active cytonemes/TM structures in glial cells and stained with Fz1 (gray) in the following genotypes (A–F) control, glioma, MMP1-RNAi, glioma MMP1-RNAi, MMP2-RNAi, and glioma MMP2-RNAi brain sections. (G) Quantification of Fz1 average pixel intensity staining ratio between ihog+ and ihog–domains. (H) Quantification of glial/glioma network volume expansion. (I) Survival curve of adult control, glioma, glioma MMP1-RNAi, and glioma MMP2-RNAi flies after a number of days of glioma induction and progression. (J) Neurons from the larval neuromuscular junction were stained with Nc82 (brp, in gray) to reveal and quantify the synaptic active zones. Upon glioma induction, the number of synapses is reduced when compared with the control. The number of synapses is restored toward control levels upon knockdown of MMP1 or MMP2. (K) Model: Glioma cells produce a network of TMs that grow to reach neighboring neurons. Intimate membrane contact facilitates neuronal-Wg sequestering mediated by glioma Fz1 receptor. Glial cells are initially transformed into malignant GB upon EGFR and PI3K pathways constitutive activation; afterward GB cells establish a positive feedback loop including TMs, Wg signaling, JNK, and MMPs. Initial stimulation of actin cytoskeleton remodeling via EGFR/PI3K enables initial expansion of TMs; as a consequence, Fz1 receptor accumulation in TMs mediates neuronal-Wg depletion and Wg signaling up-regulation in the GB cells, which activates JNK in GB. As a consequence, MMPs are up-regulated and facilitate further TM infiltration in the brain; hence the GB TM network expands and mediate further wingless depletion to close the loop. Error bars show SD; *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0001, or ns for nonsignificant. Scale bar size is indicated in this and all figures. The data underlying this figure can be found in S1 Data. Genotypes: (A) repo-Gal4, ihog-RFP/UAS-lacZ, (B) UAS-dEGFRλ, UAS-dp110CAAX;; repo-Gal4, UAS-ihog-RFP, (C) UAS-MMP1-RNAi; repo-Gal4, ihog-RFP, (D) UAS-dEGFRλ, UAS-dp110CAAX; UAS-MMP1-RNAi; repo-Gal4, UAS-ihog-RFP, (E) UAS-MMP2-RNAi; repo-Gal4, ihog-RFP, (F) UAS-dEGFRλ, UAS-dp110CAAX; UAS-MMP2-RNAi; repo-Gal4, UAS-ihog-RFP. EGFR, Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor; Fz1, Frizzled1; GB, glioblastoma; Ihog, interference hedgehog; JNK, cJun N-terminal kinase; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase; RFP, Red Fluorescent Protein; TM, tumor microtube; Wg, wingless.