Figure 1.
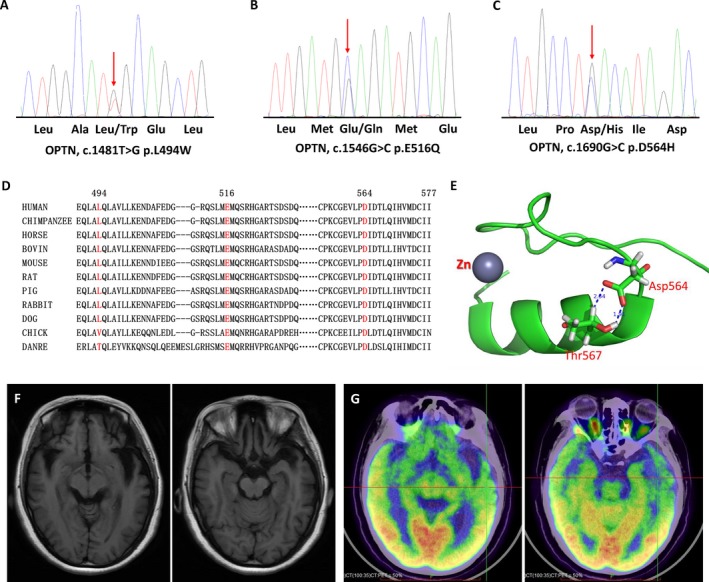
Sequencing chromatograms and pathogenicity analysis of the OPTN mutations. Sequencing chromatograms of the OPTN p.L494W (A), p.E516Q (B) and p.D564H (C) mutation. (D) Evolutionary conservation of the p.L494W, p.E516Q and p.D564H mutation in OPTN. L494, E516, and D564 are highly conserved across species. (E) Structure analysis of p.D564H mutation. The structure analysis is based on the atomic NMR model of human Optineurin (PDB code 2LO4). The amino acids position was renumbered according to the full length of OPTN protein (NM_021980). This segment of the OPTN protein is the zinc finger domain. The Asp564 is located at the transition point from coil to helix. The side chain delta 1 and delta 2 oxygen atoms of Asp564 form tightly coupled hydrogen bonds with the Thr567, as represented by the dash line the labeled distance 2.34Åand 1.91Å. The replacement of Asp564 by a bulky Histidine residue would very likely introduce sterechemical clashes, thus affect zinc finger domain stability. (F) Brain MRI of the patient with OPTN p.E516Q mutation showed brain atrophy especially in bilateral frontal and temporal lobes. (G) PET of the patient with OPTN p.E516Q mutation revealed hypo‐metabolic changes in several brain regions, especially in bilateral frontal and temporal lobes.
