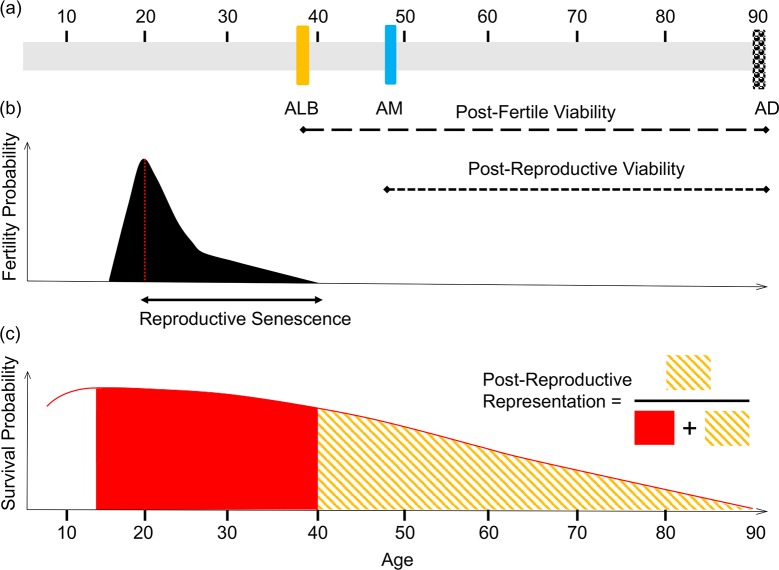
Fig 1. Measuring postreproductive life span: The differences between postfertile viability, postreproductive viability, reproductive senescence, and a postfertile life stage.
(A) A woman’s hypothetical life span. Postfertile viability is defined as the length of time between ALB, which typically occurs between 39 and 41 years (reviewed in [69]) and AD. By contrast, postreproductive viability is defined as the length of time between AM and AD. (B) Reproductive senescence. Reproductive senescence corresponds to fertility decline over age, which culminates in the cessation of fertility (ALB). (C) Postreproductive representation. The extent to which a species displays a postreproductive life stage is informed by the ratio of postfertile adult years lived relative to the total adult years lived. For the sake of simplicity, the age at the onset of actuarial senescence was set at the age at first reproduction [7]. AD, age at death; ALB, age at last birth; AM, age at menopause.