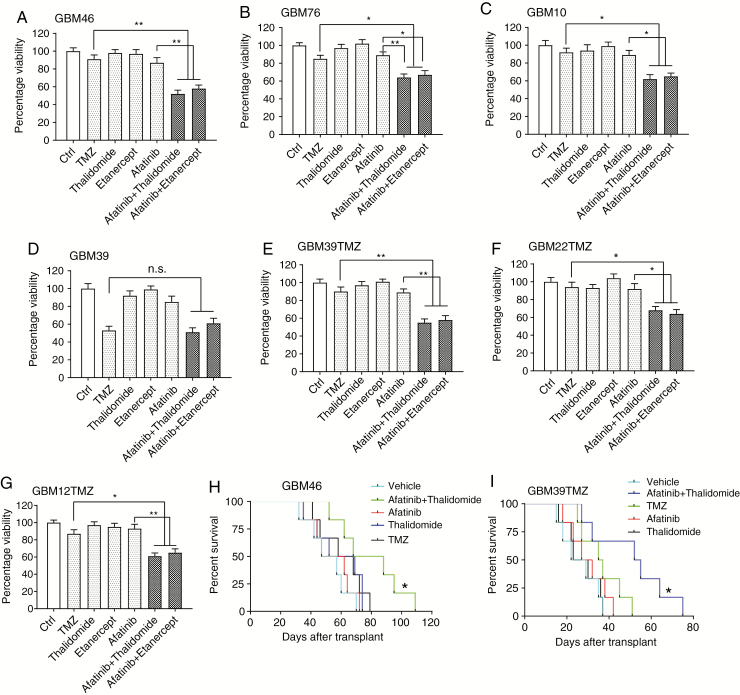
Fig. 6.
EGFR plus TNF inhibition remains effective in recurrent GBMs and GBMs rendered experimentally resistant to TMZ. (A–C) AlamarBlue assay in recurrent GBM46, GBM76, and GBM10 cells. Cells were treated with TMZ (10 μM), afatinib (1 μM), etanercept (100 μg/mL), or thalidomide (1 μM), each drug alone or 2 drugs: afatinib plus thalidomide/etanercept for 72 hours, followed by alamarBlue cell viability assay. Dimethyl sulfoxide was used as a control (Ctrl). (D) A similar experiment was conducted in GBM39 cells, except that the afatinib concentration is 1 µM. (E–G) Acquired TMZ-resistant GBM39TMZ, GBM22TMZ, and GBM12TMZ cells were treated with TMZ (10 μM), afatinib (1 μM), etanercept (100 μg/mL), or thalidomide, each drug alone or 2 drugs: afatinib plus thalidomide/etanercept for 72 hours, followed by alamarBlue cell viability assay. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; n.s., not significant. (H) Combined treatment of afatinib (50 mg/kg) and thalidomide (150 mg/kg) prolonged survival in GBM46 orthotopic model (n = 6). A comparison was done between EGFR plus TNF inhibition and TMZ (50 mg/kg). P = 0.045. (I) The same treatments were used in GBM39T orthotopic model (n = 8 mice per group). TMZ versus afatinib plus thalidomide: P = 0.019. Kaplan–Meier survival curves were calculated using GraphPad Prism 7. Statistical significance was verified by the log rank test. *P < 0.05.