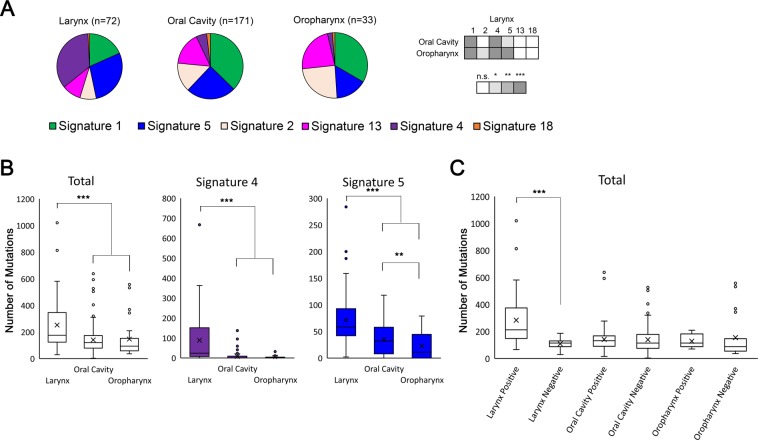
Figure 1.
COSMIC signature 4 contributes to significantly higher mutation burden in larynx compared with oral cavity and oropharynx SCC. (A) Pie charts show the proportion of all single nucleotide mutations attributed to each of the six COSMIC mutation signatures identified in head and neck SCC for each of the three major sub-sites. n = total number of individual tumors for each sub-site. Signatures 1, 2, 4, 5, 13, and 18, are derived from version 2 of COSMIC mutational signatures. Signatures 1 and 5 are of unknown etiology and associated with age, signature 2 and 13 are associated with APOBEC mutagenesis, signature 4 is associated with tobacco smoke exposure, and signature 18 is associated reactive oxygen species. Matrix to the right of pie charts shows statistical significance of individual COSMIC signature weight (normalized to mutation number) comparing larynx with oral cavity and oropharynx tumors. No significance was seen comparing signature weight between oral cavity and oropharynx tumors for any of the six signatures. n.s. = no significance. (B) Box and whisker graphs show total number of single nucleotide mutations as well as those attributed to signature 4 and signature 5, identified in each of the major sub-sites of HNSCC. (C) Total mutations stratified by the presence (positive) or absence (negative) of signature 4 mutations. x = mean. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.