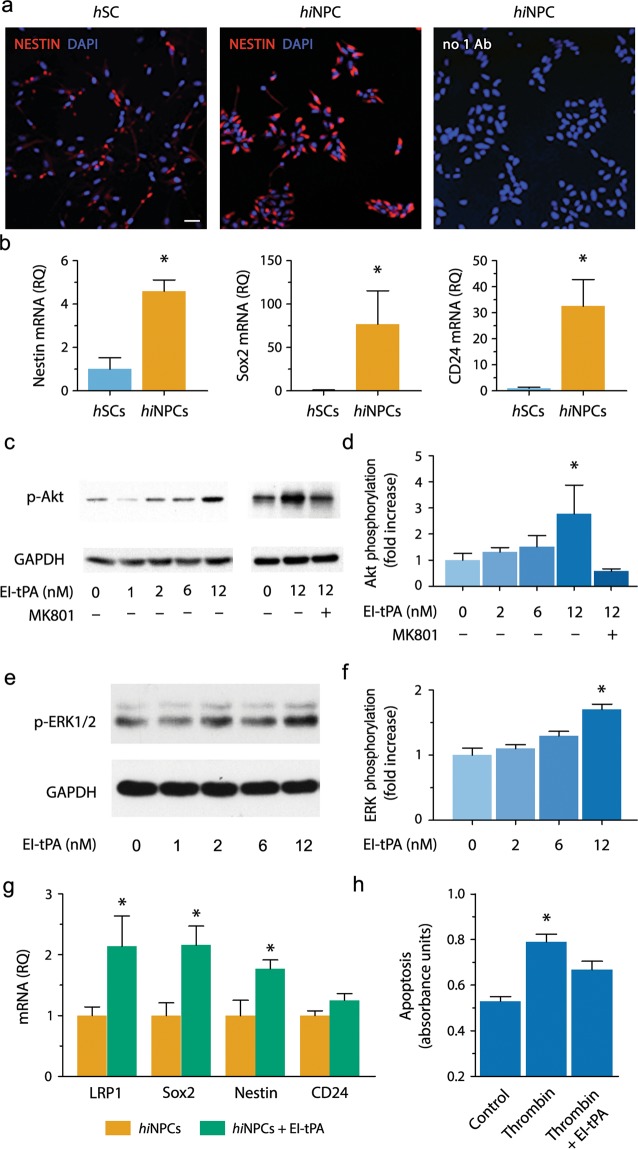
Figure 1.
Bioactivity of EI-tPA in hiNPC in vitro. (a) Representative IF microscopy images of hiNPCs and hSCs immunostained to detect Nestin (red) and labeled with DAPI (blue) (n = 3 per group). As a control, hiNPC were incubated with secondary antibody only and with DAPI (right-hand panel). Scale bar 40 µm. (b) mRNAs encoding Nestin, Sox2, and CD24 in hiNPC and hSCs. Human EID2 mRNA was quantified as a normalizer (*P < 0.05 by Student's t-test, mean ± SEM; n = 4). (c) hiNPC were treated with EI-tPA (0–12 nM) for 15 min (n = 3 independent studies). In some wells, MK801 (1 µM) was added prior to EI-tPA (n = 2 independent studies). Equal amounts of cellular protein (20 µg) were subjected to immunoblot analysis to detect phospho-Akt and GAPDH. (d) Akt phosphorylation immunoblots were subjected to densitometry. Levels of phospho-Akt were standardized using GAPDH (*P < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA, Neuman Keuls post hoc test, mean ± SEM). (e) hiNPC in culture were treated with EI-tPA (0–12 nM). ERK1/2 phosphorylation and total ERK1/2 were determined. (f) Densitometry analysis of phospho-ERK1/2 and GAPDH (*P < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA followed by Neuman Keuls post hoc test, mean ± SEM; n = 3 independent experiments). (g) Cultured hiNPC were treated El-tPA (12 nM) or vehicle for 48 h. RT-qPCR was performed to compare mRNA levels for Nestin, Sox2, CD24, and LRP1 (*P < 0.05 by Student t-test, mean ± SEM; n = 5 replicates per group;). (h) hiNPC were treated with thrombin (5 units/mL), in the presence of vehicle or 12 nM EI-tPA for 18 hours. Cell extracts were analyzed using the Cell Death ELISA (*P < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA with a Neuman Keuls post-hoc test, mean ± SEM; n = 3–8 replicates per group).