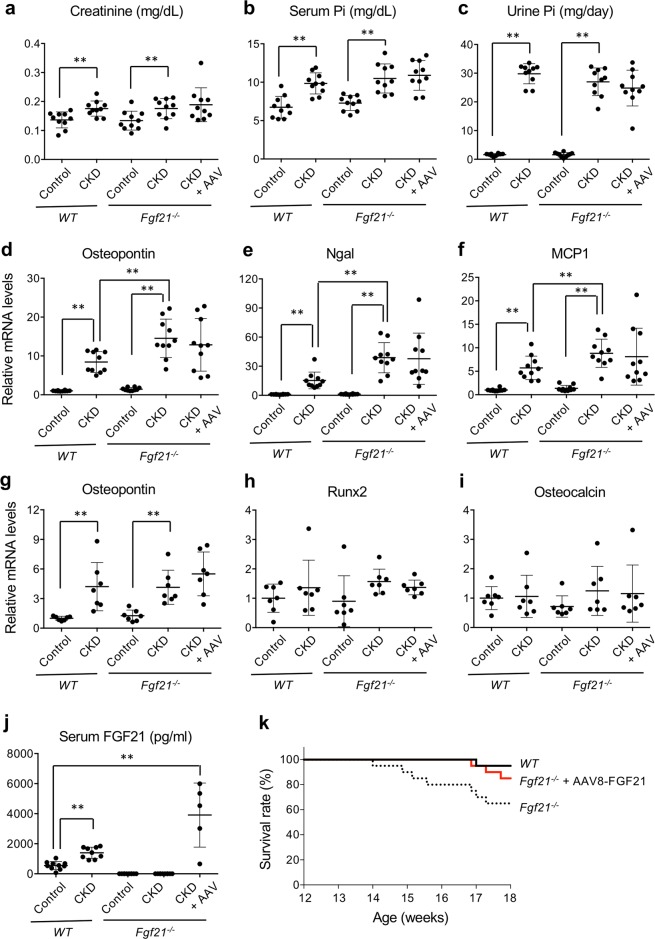
Figure 1.
FGF21 is required to survive CKD. Wild-type mice (WT) and FGF21 knockout mice (Fgf21−/−) were subjected to either uninephrectomy followed by high phosphate diet feeding (CKD) or sham-operation followed by normal diet feeding (Control). Ten out of the 20 Fgf21−/− CKD mice were administered with the AAV8-FGF21 vector when the high phosphate diet feeding was started at 12 weeks of age (CKD + AAV). Serum creatinine (a), serum phosphate (b), and urine phosphate (c) were indicated. Relative mRNA expression levels of osteopontin (d), Ngal (e), and MCP1 (f) in the kidney were indicated. Relative mRNA expression levels of osteopontin (g), Runx2 (h), and osteocalcin (i) in the aorta were indicated. (j) Serum FGF21 levels. The bars indicate mean ± SD, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05 by t-test. (k) Survival curves of CKD mice. FGF21 knockout mice (Fgf21−/−) showed poorer prognosis than wild-type mice (WT, P = 0.017 by log-rank test), but survived as well as WT when treated with the AAV8-FGF21 vector at 12 weeks of age.