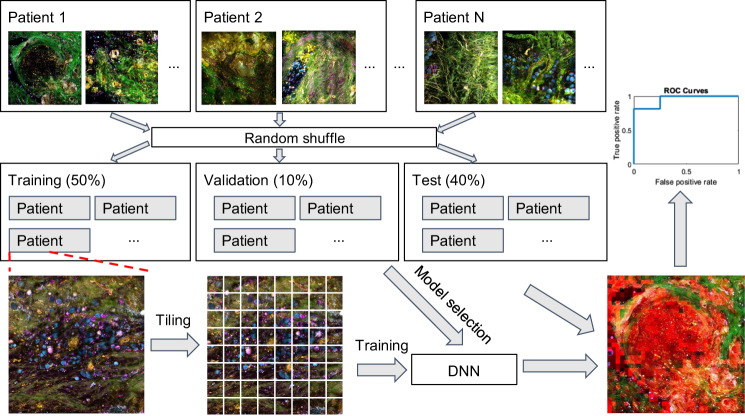
Fig. 2.
Deep-learning framework for training and evaluating a model to recognize cancer tissue from normal tissue. Subjects were randomly divided into three sets: training, validation, and test sets. Each subject was represented by multiple virtual slides, and each slide was sliced into smaller ‘tiles’. Model selection was done based on the performance in the validation set. After learning and selection, the model was applied to tiles in the previously unseen test data. This produces a heatmap of each slide showing the confidence of the model in each tile being cancerous. Per-tile accuracy was obtained from this heatmap (across all slides from test subjects) and per-slide accuracy was obtained by averaging tile-level predictions across the entire slide.