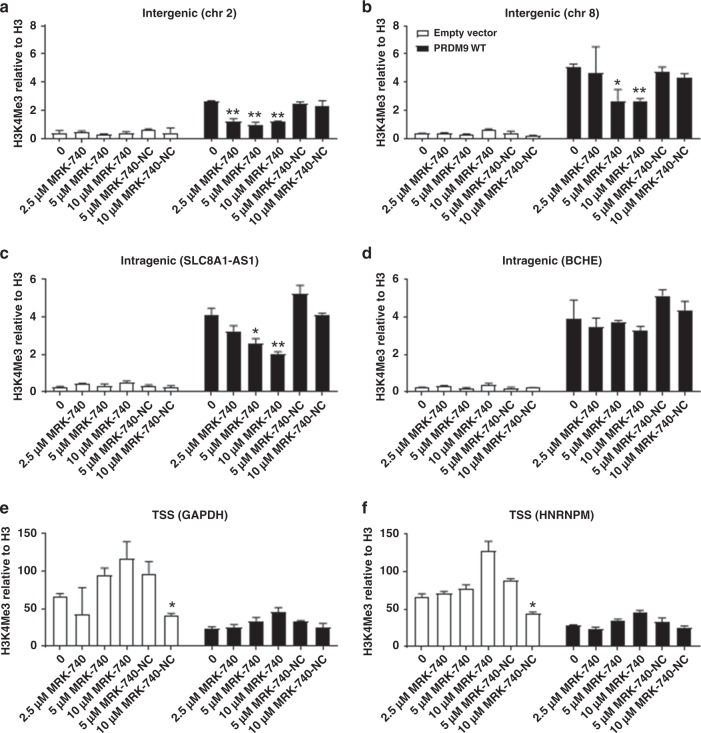
Fig. 7. Concentration-dependent inhibition of PRDM9-dependent H3K4 trimethylation using MRK-740.
ChIP qPCR analyses of H3K4me3 methylation levels of known PRDM9-bound loci and control loci. Cells transfected with empty vector control, or a vector overexpressing wild-type PRDM9 were treated with DMSO, increasing concentrations of MRK-740 or MRK-740-NC. Concentrations used (µM) are indicated below each plot. (a–d) represent reported loci of PRDM9 methylation26; (e, f) are transcriptional start sites (TSSs) which are not known loci of PRDM9 methylation. Data are normalized to total H3 and are presented as the mean ± upper and lower limits from two replicates. Representative plots of two independent experiments are shown in this figure. The coordinates and the genomic features associated with the assayed loci are indicated above each plot. Left Tailed Student's t-tests were performed by comparing DMSO (0 µM) treated cells to compound treated cells that have been transfected with the same plasmids. *p-value < 0.05 and **p-value < 0.01. Note that here we show a representative of two independent experiments (mean ± s.d of technical replicates) for our ChIP-qPCR experiments. Data obtained using this technique are inherently noisy due to stochastic differences in gene activity/histone positioning. Data are thus typically presented as representative rather than averaged. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.