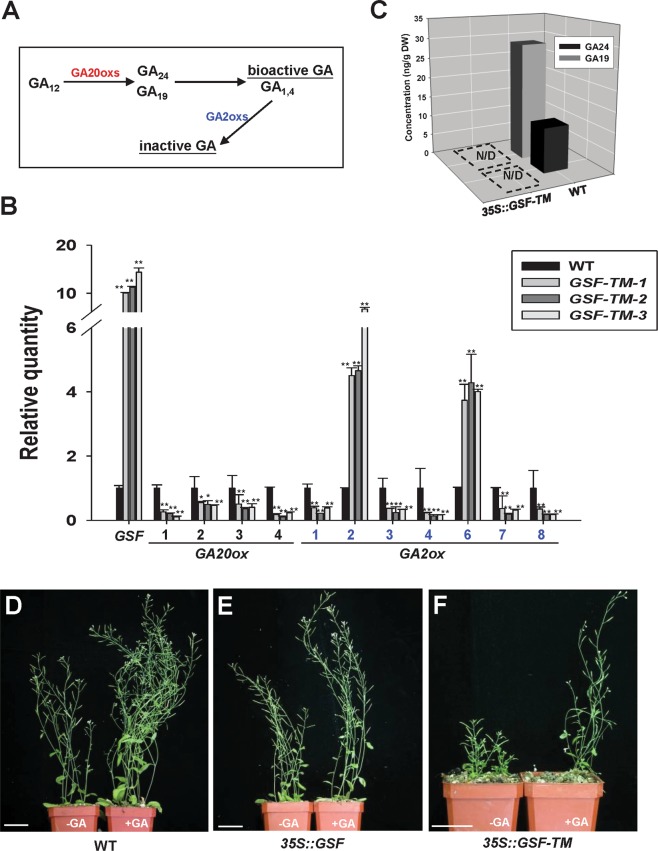
Figure 5.
Transcript levels of GA metabolic pathway genes and the external application of GA in 35S::GSF-TM transgenic plants. (A) Schematic diagram for the gibberellin biosynthetic pathway. GA20-oxidases (GA20oxs) participate in the biosynthesis of the major bioactive GAs (GA1 and GA4) from the intermediates, such as GA19 and GA24. GA2-oxidases (GA2oxs) are involved in the late steps in the metabolic pathway to convert bioactive GAs into inactive GAs. (B) Detection of the expression for GSF, GA20oxs (1–4) and GA2oxs (1,2,3,4,6,7,8) in one wild-type (WT) plant and three severe (GSF-TM-1, 2, 3) 35S::GSF-TM transgenic Arabidopsis plants using real-time quantitative RT-PCR. The expression level relative to wild-type plants is presented. Error bars represent standard deviation. The asterisks indicate a significant difference from the wild type (WT) value (*P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01) by Student’s T-test. (C) Detection of the concentrations of GA19 and GA24, intermediates in a bioactive GA biosynthesis pathway in wild-type (WT) and 35S::GSF-TM Arabidopsis. N/D indicates that a signal was not detected in the samples. (D–F) External supply of GA in the wild-type (D), 35S::GSF (E) and 35S::GSF-TM (F) plants. The shoot elongation was clearly observed in the wild-type (D, right) and 35S::GSF plants (E, right) after GA treatment. The significant elongation of the inflorescence (F, right) was also observed in the GA-treated 35S::GSF-TM plants. Bar = 35 mm.