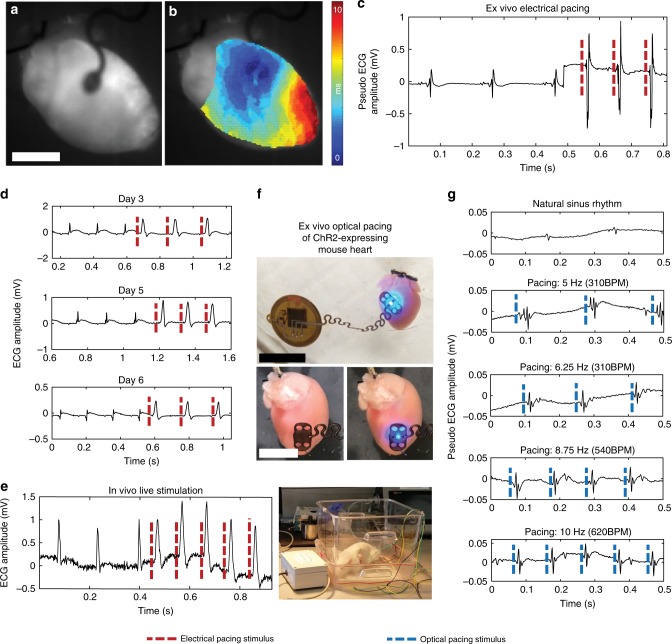
Fig. 5. Electrical and optogenetic pacing capabilities.
a Mouse hearts were electrically stimulated by the device ex vivo (scale bar 0.5 cm). b The time course of pacing activation was tracked using the membrane potential to show anisotropic conduction by optical mapping. c Far-field ECG pacing demonstrates capture of the heart during ex vivo pacing. d Chronic in vivo pacing of rat hearts was achieved with implanted pacemakers for up to 6 days. e Rat hearts were captured (right) while the animal was freely moving. f Ex vivo ChR2-expressing mouse hearts were optically paced at the anterior epicardial surface of the left ventricle (top) (scale bar 1 mm) in the off (bottom left) and on (bottom right) configuration (scale bar 0.5 mm). g Ex vivo ChR2-expressing mouse hearts were able to be captured at 280, 310, 540, and 620 b.p.m.