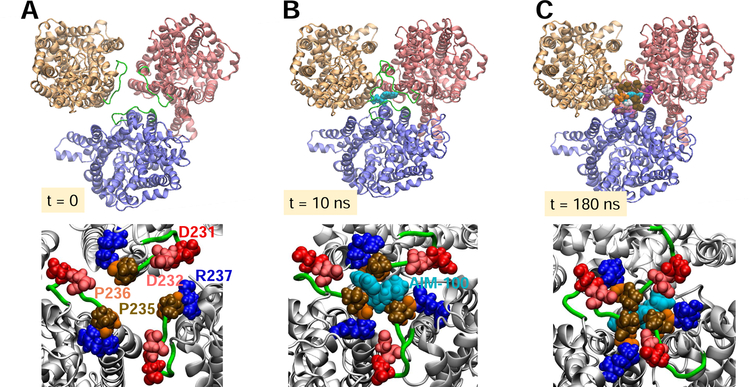
Fig. 3. EL2b loop interactions drive the tight packing of the protomers, assisted by AIM-100 binding.
(A-C) Time evolution of protomer positions (top, viewed from EC region) and interfacial interactions (bottom) at t = 0, 10, and 180 ns to stabilize the trimer-W238. The surrounding lipids and other molecules included in simulations (see Fig 2A) are omitted for clarity. (A) Initially, protomers are separated by ~50 Å (center of mass distances) (B) AIM-100 (cyan, vDW), originally 25 Å away from the binding site, migrated to locate the interfacial region at the EC-exposed vestibule, stabilized by P235 and P236. (C) Inter-subunit salt bridges D231/D232-R237 consolidate the trimeric packing and the closer assembly of the protomers whose mass center distances are reduced by 5Å.