Fig. 1. HBV mono-infection, HBV/HDV co-infection, and HBV/HDV super-infection kinetics in SACC-PHHs.
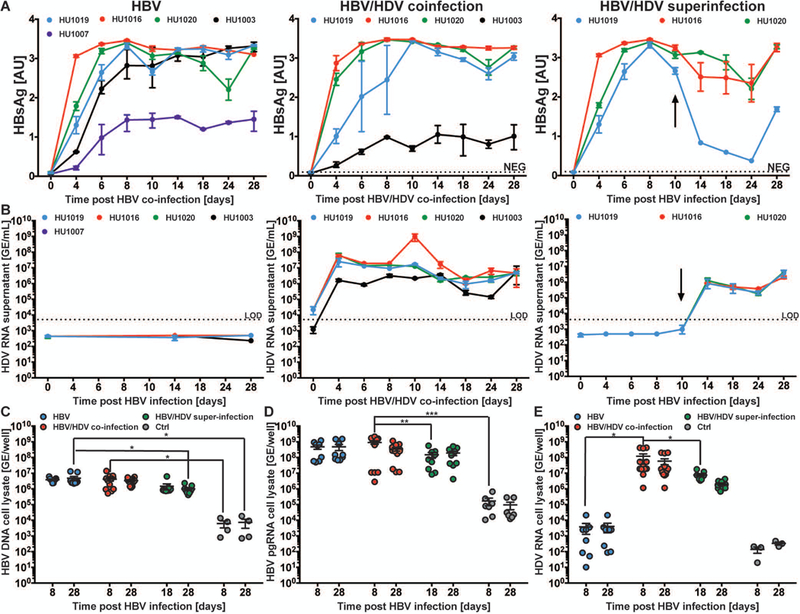
SACC-PHHs were infected with either HBV, HBV/HDV (co-infection), or were first persistently infected with HBV and then with HDV (super-infection). (A) Longitudinal HBsAg ELISA data. (B) HDV RNA RT-qPCR data from supernatants. HBV DNA (C), HBV pgRNA (D), or HDV RNA (E) in the cell lysates. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined using ANOVA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001.
