Fig. 7: Induction of innate immunity by poly(I:C) treatment leads to suppression of HBV.
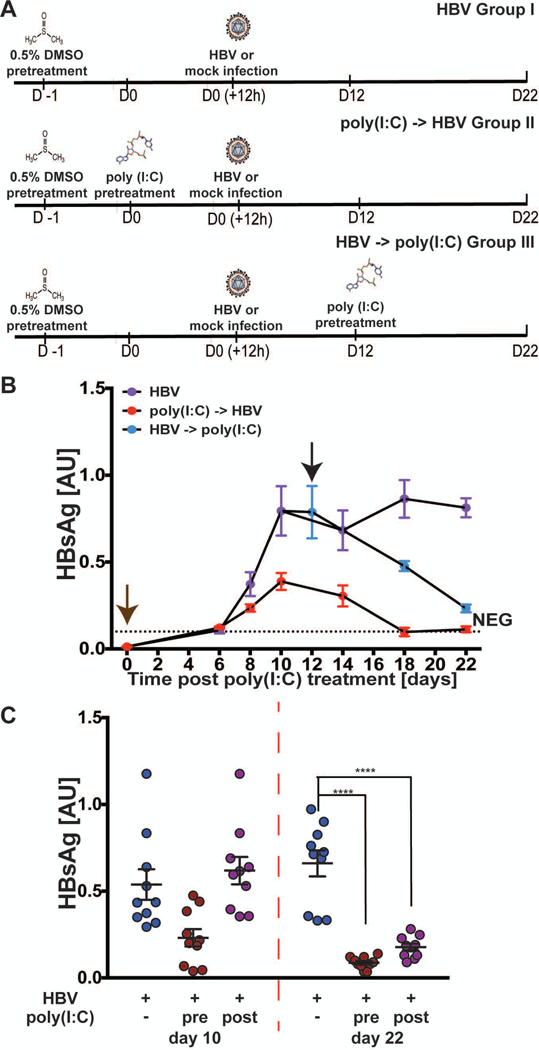
(A) Schematic of experimental time course for poly(I:C)-transfected SACC-PHHs infected with HBV. Longitudinal measurements of HBsAg by ELISA in supernatants (B-C) of SACC-PHHs +/− poly(I:C) as shown in panel A. Brown and black arrows indicate poly(I:C) transfection either pre- or post-establishment of persistent infection, respectively. Co-infected SACC-PHHs +/− poly(I:C) were lysed 12 and 22 dpi. A separate set of pre-infected SACC-PHHs for each donor were also lysed. Statistical significance was determined using ANOVA. ****P < 0.0001.
