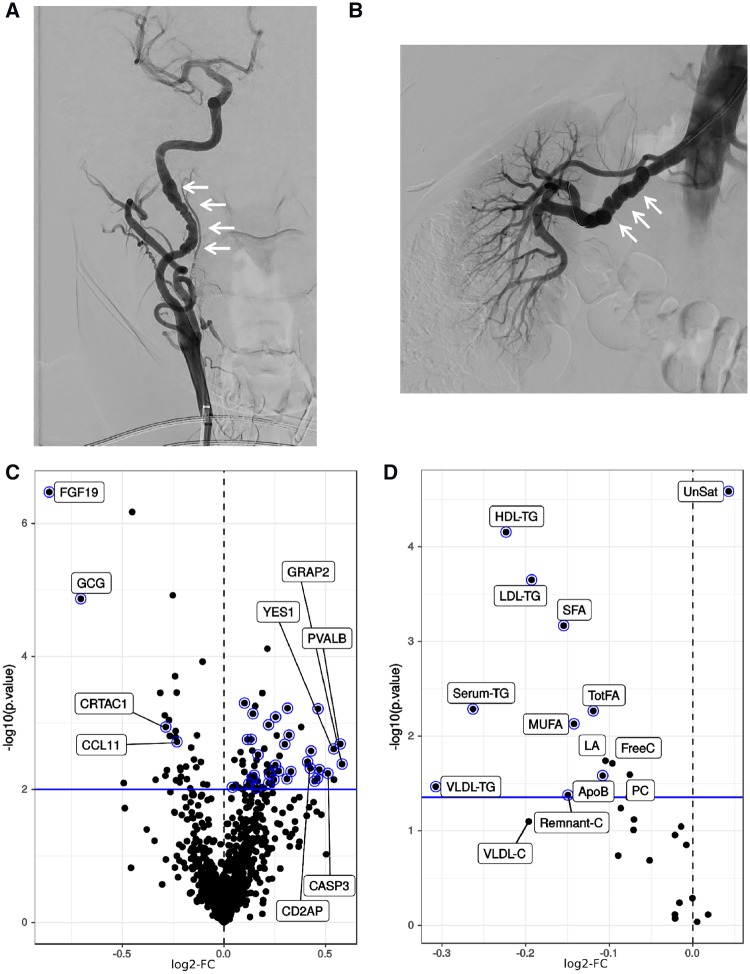
Figure 1.
Typical multifocal FMD and differential protein levels between FMD cases and matched healthy controls in the discovery cohort dataset. (A) Catheter-based angiographic image representative of the typical appearance of multifocal FMD affecting the carotid artery. (B) Typical catheter-based angiographic appearance of multifocal FMD affecting the renal artery, with so called ‘string-of-beads’ appearance. (C) Volcano plot of the differential protein level analysis comparing FMD patients to healthy controls; log2-fold change (log2-FC) on the horizontal axis, -log10 (P-value) on the vertical axis; the horizontal blue line marks the 10% FDR significance threshold. Selected proteins with large effect size or of further interest are labelled. Proteins that were subsequently validated (in the separate validation cohort) are represented with a blue halo. (D) Volcano plot of the differential lipid and lipoprotein level analysis in a fully adjusted model comparing FMD patients to healthy controls (co-variates were age, BMI, statin use, and non-statin lipid lowering medication use); log2-FC on the horizontal axis, -log10 (P-value) on the vertical axis; the horizontal blue line marks the 10% FDR significance threshold. Selected lipid and lipoprotein species with largest effect size are labelled. Lipids that were subsequently validated (in the separate validation cohort) are represented with a blue halo. ApoB, Apolipoprotein B; FreeC, free cholesterol; HDL-TG, triglycerides in HDL; LA, 18:2 linoleic acid; LDL-TG, triglycerides in LDL; MUFA, monounsaturated fatty acids 16:1, 18:1; PC, phosphatidylcholine and other cholines;. Remnant-C, remnant cholesterol (non-HDL, non-LDL-cholesterol); Serum-TG, serum total triglycerides; SFA, saturated fatty acids; TotFA, total fatty acids; UnSat, estimated degree of unsaturation of all fatty acids (the numeric value is an estimate of the average number of double bonds in the fatty acid chains); VLDL-C, total cholesterol in VLDL; VLDL-TG, triglycerides in VLDL.