FIG 8.
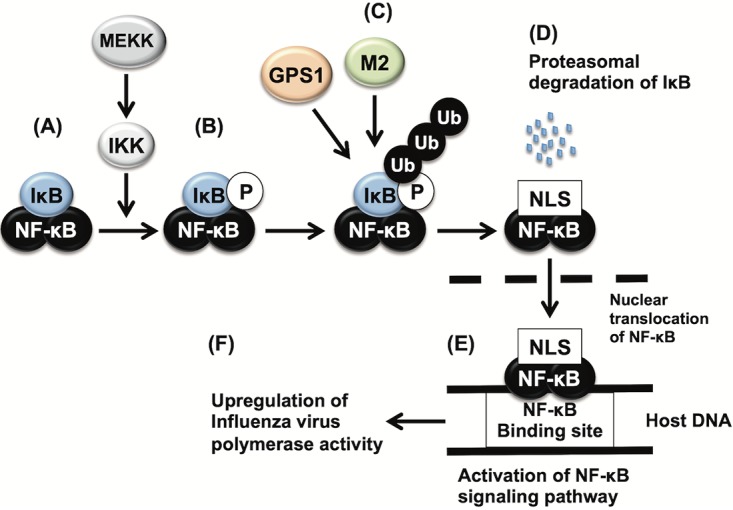
Hypothetical scheme of the role of GPS1 in influenza virus polymerase activity. The results of our study suggest that GPS1 plays a role in influenza virus polymerase activity via the NF-κB signaling pathway. (A) IκB inhibits the nuclear localization of NF-κB by masking the nuclear localization signal of NF-κB. (B) IκB is phosphorylated by IκB kinase (IKK). (C) GPS1, possibly with M2, supports the polyubiquitination of IκB. (D) Polyubiquitinated IκB is recognized by proteasomes and subjected to proteasomal degradation, and the NLS of NF-κB is exposed. (E) NF-κB translocates to the nucleus, and the NF-κB signaling pathway is activated. (F) Finally, the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway results in the upregulation of influenza virus polymerase activity. Ub, ubiquitin.
