Table 4.
Selected antimicrobial systems based in cationic polymers and antibiotics.
| Schematic Representation of the Antimicrobial Polymer | Antibiotic | Microorganism Tested | Synergistic Effect | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
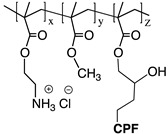
|
Ciprofloxacin (CPF) | E. coli | Integrity of the cell membrane was disrupted by hydrophobic moieties (in an optimal concentration). CPF inhibits the activity of the bacterial DNA gyrase, which leads to bacterial cell death. | [161] |
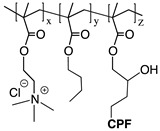
|
Ciprofloxacin (CPF) | E. coli | [162] | |
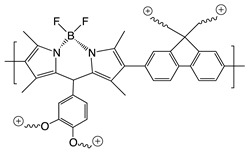
|
Polypeptide antibiotics: Polymyxin B Polymyxin R |
E. coli | Combination of cationic conjugated polymers (CCPs) with polypeptide antibiotics facilitates and accelerates the rupture and collapse of bacterial membranes. | [173] |
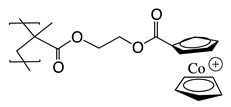
|
Penicillin-G Amoxicillin Ampicillin Cefazolin |
MRSA | Adsorption of metallopolymer to the negatively charged MRSA surface which promotes damage in the cell walls and at the same time allows the release of complexed antibiotic. | [169] |
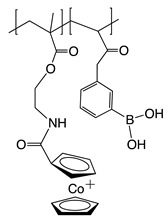
|
Penicillin-G |
E. coli
P. aeruginosa P. vulgaris |
Phenylboronic acid binds to peptide-glycan via boron-polyol based boronolectin chemistry, cationic cobalto-cenium moiety interact with negatively charged cell membranes and antibiotic is reinstated with enhanced vitality to attack bacteria | [170] |
