Coronary CT
|
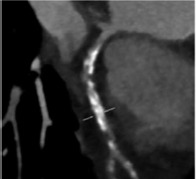
Non-invasive technique Calcium score in asymptomatic individuals Prognostic role of calcium score Calcium location along coronary vessels detected Spotty calcifications are detected
|
|
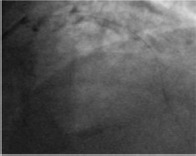
Coronary angiography
|
|
|
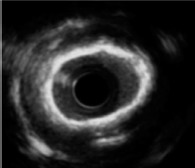
Intravascular ultrasound
|
No contrast medium Superficial and deep calcium is detected Semiquantitative grading of calcium: distribution, localisation, length, arc
|
Invasive technique Deep calcium is hidden by acoustic shadow Microcalcifications are not detected Unable to assess calcium thickness
|
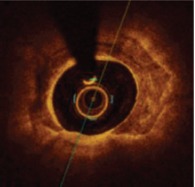
Optical coherence tomography
|
Very high resolution Calcium thickness can be measured Quantitative grading of calcium: distribution, localisation, thickness, area, volume Microcalcifications are detected
|
|







