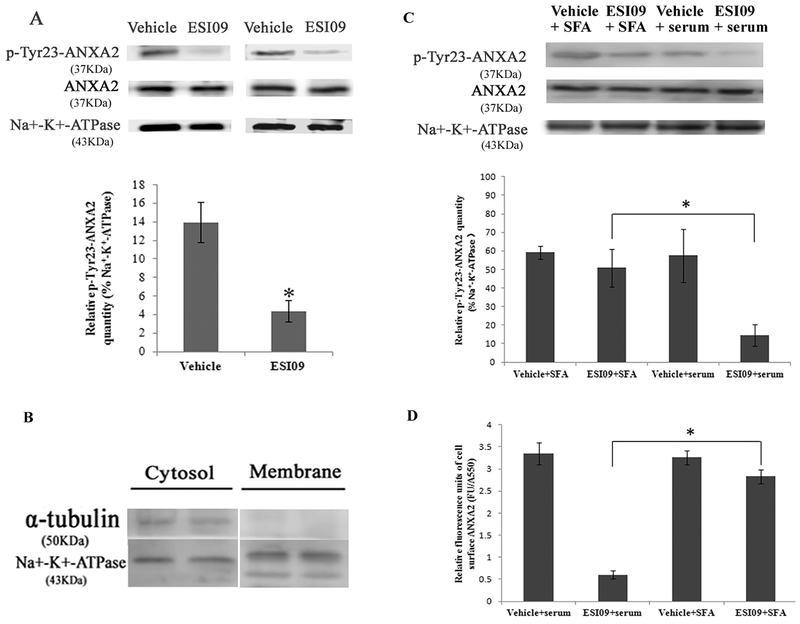
Fig. 6.
Inhibition of EPAC1 decreased tyrosine 23-phosphorylated ANXA2 in the cell membrane compartment. Representative WB (A) shows reduced expression of tyrosine 23-phosphorylated ANXA2 (p-Tyr23-ANXA2) in the membrane fractionation of ESI09-treated HUVECs (n = 4) compared with vehicle-treated HUVECs (n = 4) (P < 0.05). Densitometry was used to quantify the relative intensity of tyrosine 23-phosphorylated ANXA2-specific immunoblots normalized by the indicated loading controls. The purity of the isolation of cell membrane proteins was evaluated (B). Representative WB (C, n = 3 for each group) shows restored expression of tyrosine 23-phosphorylated ANXA2 in the membrane fractionation of ESI09-treated Src family activator (SFA)-exposed HUVECs, compared to ESI09-treated HUVECs (* P < 0.05). An impermeable cell-based ELISA assay shows increased relative fluorescence units of cell surface ANXA2 in ESI09-treated SFA-exposed HUVECs, compared to ESI09-treated group (D, n = 4 for each group) (*P < 0.05). All experiments were repeated three times.