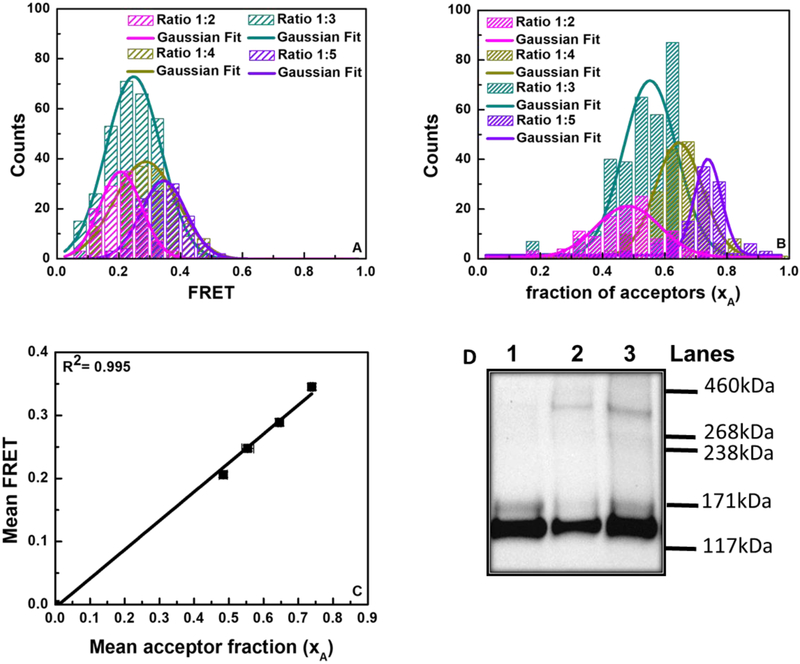
Figure 3.
FRET and cross-linking data demonstrating full-length Trk-A dimer-formation. (A) Histograms of measured FRET efficiencies at four different donor to acceptor ratios (1:2, 1:3, 1:4, and 1:5). (B) Histograms of acceptor fractions (xA) for the four donor to acceptor ratios. (C) Average FRET efficiencies as a function of average acceptor fractions (xA). The standard errors, which are smaller than the symbols, are also shown. The linear dependence is indicative of dimer formation. (D) Trk-A Western blot in the absence and presence of a chemical cross-linker. Lane 1: Trk-A; Lane 2: Trk-A + cross-linker; Lane 3: Trk-A + hß-NGF + cross-linker. The molecular weight of monomeric, mature, fully glycosylated TrkA is ~ 140 kDa, and thus the molecular weight of fully mature Trk-A-YFP is ~170 kDa. The intense lower molecular weight band corresponds to immature, partially glycosylated TrkA found in the ER and Golgi. The fully mature Trk-A-YFP dimer molecular weight is ~340 kDa.