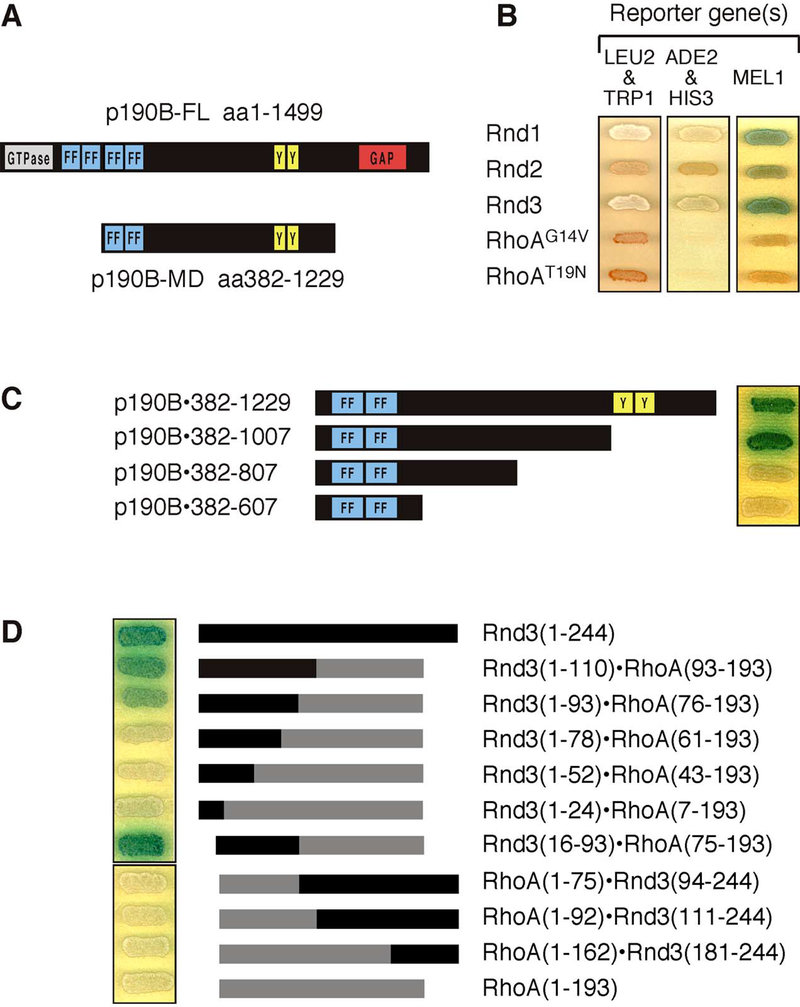
Figure 1: Rnd proteins interact with p190B-MD.
(A) Schematic presentation of full-length p190 and the fragment corresponding to p190B-MD isolated in the two-hybrid screen along with the known conserved domains found in these molecules, including the GTPase, FF, GAP, SH2 domain-binding (“Y”) domains.
(B) Rnd1, Rnd2, and Rnd3, but neither constitutively active (G14V) nor dominant negative (T19N) RhoA, interact with p190B-MD in the two-hybrid assay as evidenced by activation of the HIS3 and ADE2 reporter genes (growth) as well as the MEL1 reporter (blue color). The orange-red color of the yeast grown on drop-out plates results from the AH109 yeast strain being auxotroph for adenine.
(C) Truncation analysis of the Rnd3-interacting region of p190B-MD demonstrates that a fragment corresponding to amino acids 382–1007 is sufficient for mediating the interaction whereas further truncation of this fragment abrogates the activation of reporter genes.
(D) Results obtained with RhoA-Rnd3 chimeras demonstrate that amino acids 16–93 in Rnd3 are required, and in the background of RhoA, sufficient to mediate the interaction with p190B-MD as demonstrated by activation of the MEL1 reporter gene. Note that for (B) and (C), Rnd proteins are expressed as fusion proteins with the Gal4 DNA-binding domain and the p190 derivatives as a fusion with the Gal4 activation domain, whereas in (D), the assay is reversed.