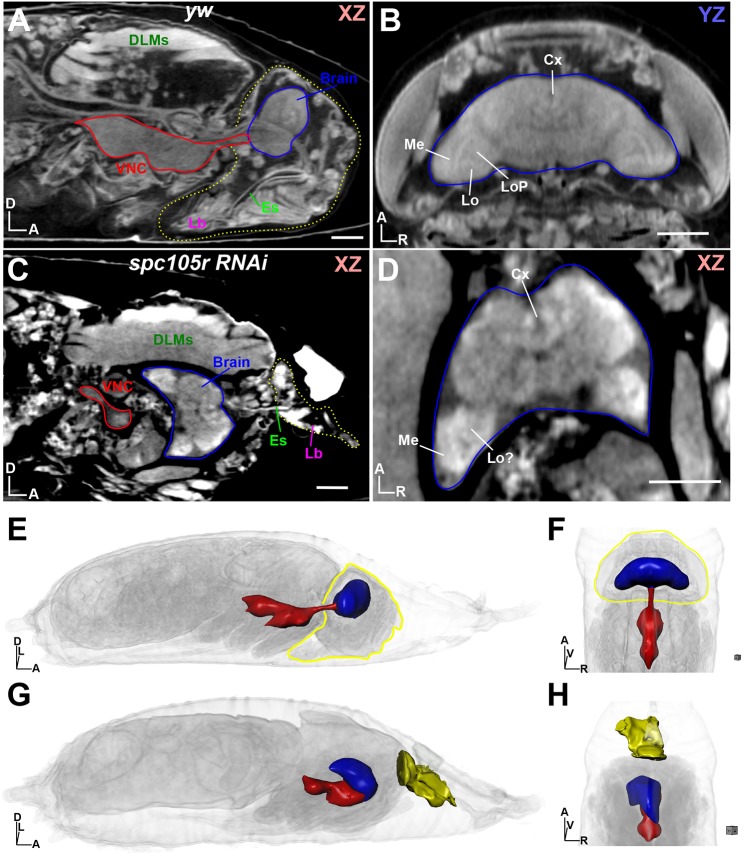
Fig. 3.
Dissection of a ‘pupal lethal’ mutation by µ-CT. (A) Wild-type (yw) pupa at stage P15 shown in xz orientation. The headcase is outlined by a yellow dotted line, with the ventral nerve cord (VNC) and brain outlined in red and blue, respectively. DLMs, dorsal longitudinal muscles; Es, esophagus; Lb, labellum. (B) View of the yw headcase from A, viewing the yz axis from the dorsal perspective. Brain is outlined in blue. Individual brain neuropils are denoted. Cx, central complex; Lo, lobula; LoP, lobula plate; Me, medulla. (C) Analysis of a pupal lethal ‘headless’ fly, resulting from RNAi depletion of spc105r (KNL1) using the eyOK107 Gal4 driver. View shown is xz, with the ‘head remnant’ outlined by a yellow dotted line. Note brain (blue outline) location in the thorax; VNC is outlined in red. (D) View of the mutant brain shown in C; neuropils are highlighted as described in B. (E) 3D view of the yw pupae shown in A; the headcase is outlined in yellow and the brain (blue) and VNC (red) are rendered as 3D surfaces. (F) Alternative view of the yw pupae from E, viewed from the dorsal perspective. (G) 3D view of the spc105r as denoted in E; head remnant containing the labellum is shown as a yellow surface. (H) Alternative view of the spc105r pupae from G, viewed from the dorsal perspective. Body axes are indicated: A, anterior; D, dorsal; L, left; R, right; V, ventral. Scale bars: 100 µm. Stained with 0.1 N iodine and scanned in slow mode at an image pixel size of 1.4 µm.