FIGURE 2.
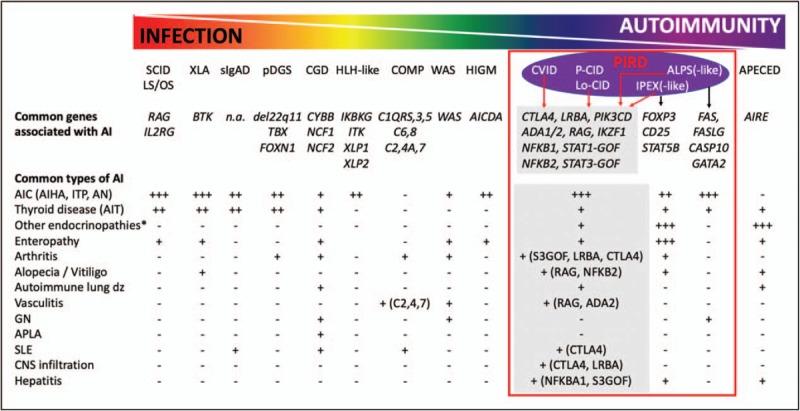
The genetic basis for infections versus autoimmunity (AI) within PIDs. An inverse gradation of infectious and autoimmune complications exists for different primary immunodeficiencies. For example, SCID patients with complete RAG deficiency or loss of IL2RG function are plagued with infections but minimal autoimmunity whereas APECED have high autoimmunity but relatively few infections. Multiple primary immune dysregulation disorders (PIRD) can be caused by the same set of genetic mutations although particular mutations favor specific diseases such as FOXP3 mutations causing IPEX-like disorder. ∗Other endocrinopathies include Addison's disease, type 1 diabetes mellitus, adrenal corticotropic hormone insufficiency, and growth hormone deficiency. COMP, complement defects; ADA1/2, adenosine deaminase 1 and 2; AIC, autoimmune cytopenia; AICDA, activation induced cytidine deaminase; AIHA, autoimmune hemolytic anemia; AIRE, autoimmune regulator; AIT, autoimmune thyroid disease; AN, autoimmune neutropenia; ALPS, autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome; APECED, autoimmune polyendocrinopathy–candidiasis–ectodermal dystrophy; APLA, antiphospholipid antibodies; BTK, Bruton tyrosine kinase; CASP10, caspase 10; CD25, cluster of differentiation 25 (interleukin-2 receptor α chain); CGD, chronic granulomatous disease; CNS, central nervous system; CVID, common variable immunodeficiency; CTLA4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4; CYBB, cytochrome B-245 β chain; FAS, FS-7 associated surface antigen; FASLG, FAS ligand; FOXN1, forkhead box N1; FOXP3, forkhead box P3; GATA2, GATA binding protein 2; GN, glomerulonephritis; HIGM, hyperimmunoglobulin M syndrome; HLH, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; IKBKG, inhibitor of nuclear factor κ B kinase subunit gamma; IKZF1, IKAROS family zinc finger 1; IL2RG, interleukin-2 receptor gamma subunit; ITP, immune thrombocytopenia; LS, leaky severe combined immunodeficiency; Lo-CID, late-onset combined immunodeficiency; LRBA, lipopolysaccharide responsive beige-like anchor protein; NCF1/2, neutrophil cytosolic factor 1 and 2; NFKB1/2, nuclear factor κ B subunits 1 and 2; OS, Omenn syndrome; P-CID, profound combined immunodeficiency; pDGS, partial DiGeorge syndrome; PIK3CD, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta; RAG, recombinase activating gene; SCID, severe combined immunodeficiency; sIgAD, secretory immunoglobulin A deficiency; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; STAT5B, signal transducer and activator of transcription 5B; STAT1/3-GOF (S1/3GOF), signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 and 3 gain-of-function mutations; TBX, T-box transcription factor; WAS, Wiskott Aldrich syndrome; XLP1/2, X-linked lymphoproliferative disease 1 and 2; XLA, X-linked agammaglobulinemia.
