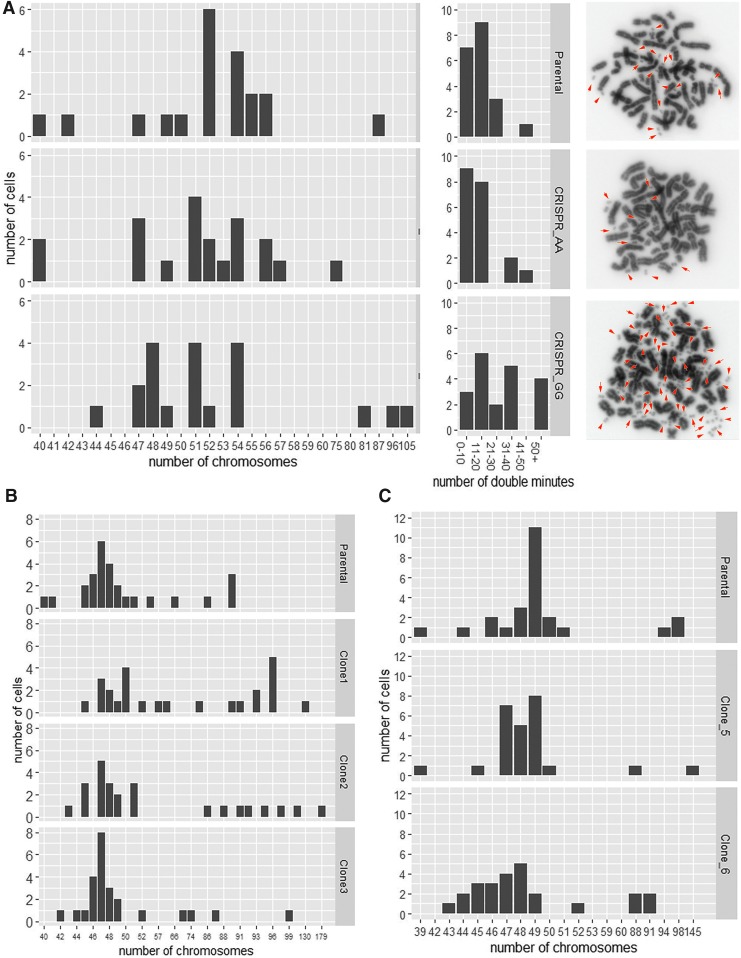
FIG. 3.
CRIPSR clones exhibit chromosomal instability. (A) Mutation of SNP rs1800734 in the MLH1 promoter in COLO320 cells. Left panel: graphs showing the chromosome counts per cell of the parental and AA and GG sequenced clones. The parental cells show a variable number of chromosomes with the modal number of 52. The mutant clones show a wider distribution and no clear model number. Middle panel: graphs showing the number of double minutes per cell. The distribution is similar between the parental and AA clones but numbers are greatly increased in GG cells. Left panel: DAPI-stained metaphase spreads showing double minutes (red arrows). (B) Reversion of mutation in POLE exon 9 in HCC2998 cells. Graphs showing the chromosome counts per cell of the parental and clones 1, 2, and 3. The parental cells have a modal number of 47 chromosomes. Clones 2 and 3 also have a modal number of 47 and similar overall distribution. Clone 1 has more variable chromosome numbers. (C) Mutation of NFE2L2 gene in SW1463 cells. Graphs showing the chromosome counts per cell of the parental and sequenced clones 5 and 6. The parental cells show a variable number of chromosomes with the modal number of 49. The mutant clones show a wider distribution and no clear modal number.