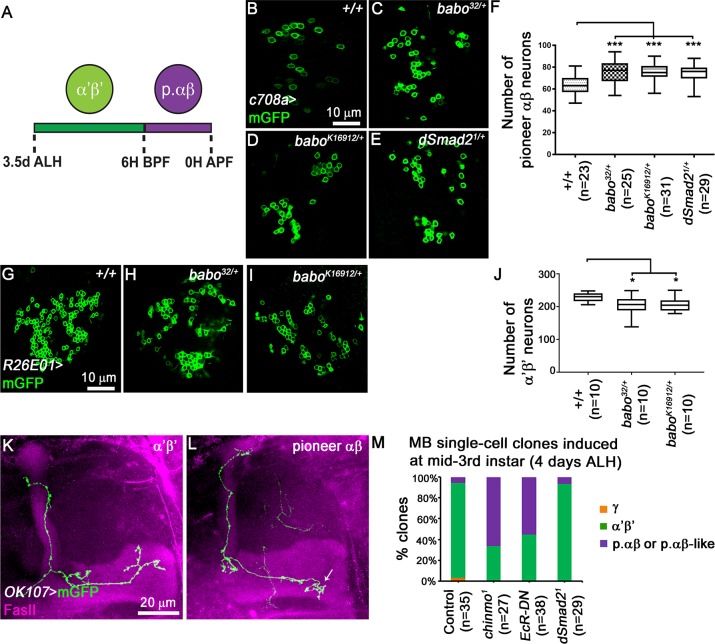
Fig 6. The numbers of pioneer αβ MB neurons is affected upon TGF-β signalling impairment.
(A) Schematic presentation of sequential production of α’β’ and p. αβ. ALH, after larval hatching; BPF, before puparium formation; APF, after puparium formation. (B-E) Single confocal section thought the cell body cluster of adult MB neurons from control (B), babo32/+ (C), baboK16912/+ (D) and dSmad21/+ (E) brains. Green: c708a-driven mGFP in B-E highlighting p. αβ neurons. (F) Quantitative analysis of MB p. αβ neuron numbers after removing one copy of babo and/or dSmad2 gene. MB p. αβ neurons were labelled by GAL4-c708a. Statistical comparison to the control: ***, p<0.001 (two tailed t test). (G-I) Single confocal section thought the cell body cluster of adult MB neurons from control (G), babo32/+ (H) and baboK16912/+ (I) brains. Green: GMR26E01-LexA-α’β’-MB-driven mGFP in G-I highlighting α’β’ neurons. (J) Quantitative analysis of the number of MB α’β’ neurons after removing one copy of the babo gene. MB α’β’ neurons were labelled by GMR26E01-LexA-R26E01. Statistical comparison to the control: *, p<0.001 (two tailed t test). (K, L) Adult axonal projections of single cell MARCM clone of α’β’ (K) and p. αβ (L) neurons. Arrow indicates the typical short medial axonal process of the p. αβ neurons [15]. (M) Percentages of different subtypes of MB neurons among control, chinmo1, OK107>EcR-DN and dSmad21 single cell clones that were induced at mid-third instar stage. chinmo1 clones were used as positive control for the identity switch phenotype [15].