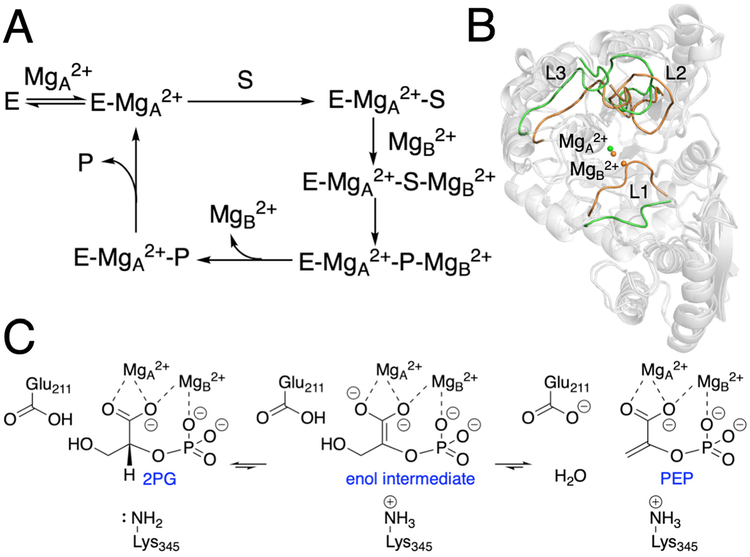
Figure 1.
Schematic depictions of (A) proposed catalytic cycle, (B) comparison between the closed and open loop states, and (C) proposed catalytic mechanism for yeast enolase. For part B, the open loop structure (green) was obtained from the PDB entry 1EBH, which corresponds to the E-MgA2+ state, and the closed loop structure (orange) was obtained from the PDB entry 1ONE, which corresponds to the E-MgA2+-S/P-MgB2+ state. The structures were superimposed by aligning the backbone Cα atoms in the protein dimer. Only chain A is shown for illustrative purposes.