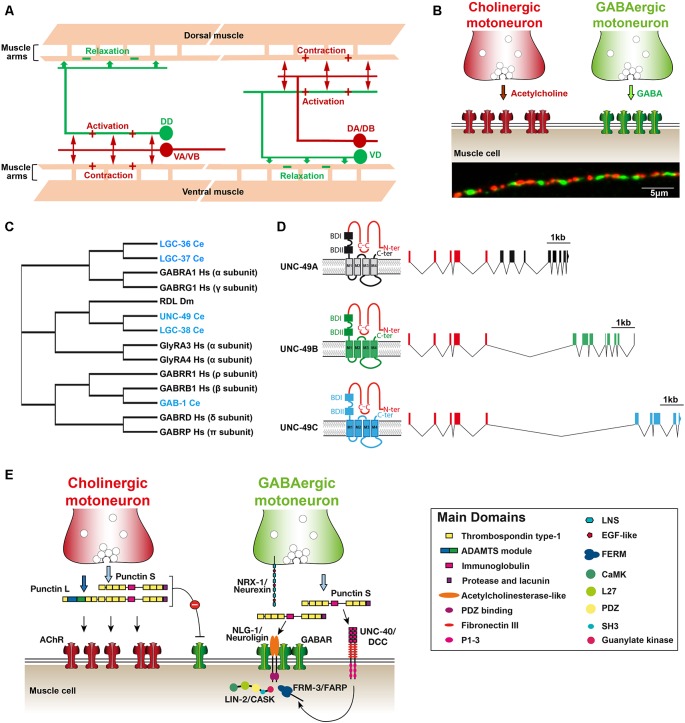
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic organization of the C. elegans neuromuscular network. Mononucleated body-wall muscle cells on the ventral and dorsal sides of the worm extend ≈5 muscle arms to contact the axon of cholinergic (red) and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic (green) motoneurons along the ventral and dorsal nerve cords, respectively. Cholinergic neurons (VA/VB and DA/DB) form dyadic synapses activating muscle cells and GABAergic motoneurons (DD and VD) that form inhibitory neuromuscular junctions (NMJs) on opposite muscle cells. (B) Distribution of excitatory and inhibitory NMJs along the ventral nerve cord. Upper panel: a schematic drawing showing that each muscle cell receives both cholinergic and GABAergic inputs. Lower panel: immunostaining of cholinergic boutons (anti-UNC-17/VAChT; red) and GABAARs (anti-UNC-49; green) at the dorsal nerve cord. (C) Cladogram showing the phylogenic relationships of the C. elegans genes encoding GABAA receptor subunits (blue). The tree was adapted from Tsang et al. (2007) and Gendrel et al. (2016). Dm, Drosophila melanogaster; Hs, Homo sapiens. (D) Schematic structure of the unc-49 locus encoding the GABAAR present at inhibitory NMJs (adapted from Bamber et al., 1999). The locus generates three distinct subunits by alternative splicing. The first five exons encode most of the extracellular N-terminal, which is common to the three subunits (red). Alternative splicing of 3′ blocks of exons encode the C-terminal part of the A,B and C subunits (black, green and blue, respectively). Putative GABA binding sites (BD) and transmembrane segments are distinct between the different subunits. (E) Working model of GABAAR clustering at NMJ in C. elegans. See the main text for discussion of the model. ADAMTS, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin; P1-3, protein binding domain 1, 2 and 3; LNS, laminin-neurexin/sex hormone-binding globulin; EGF, epidermal growth factor; FERM, (4.1, ezrin, radixin, moesin) family; SH3, src homology 3 domain; FARP, FERM, ARH/RhoGEF and pleckstrin domain protein; CASK, calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase.