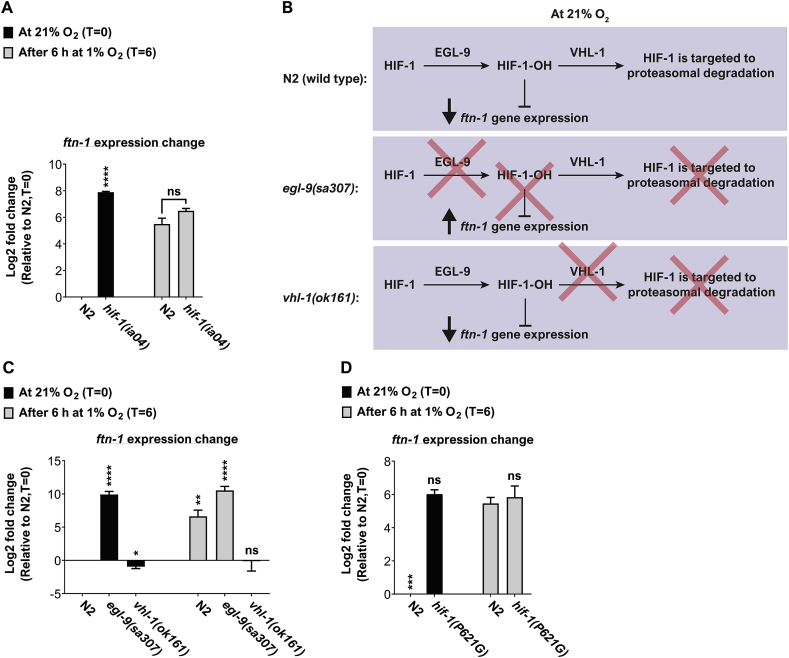
Fig. 5.
HIF-1 is not required for ftn-1-upregulation at 1% O2. (A) Bar graphs presenting the expression of ftn-1 at 21% O2 and after 6 h exposure in 1% O2. Asterisks indicate significance for comparisons with N2 animals at the beginning of the experiments (21% O2, time = 0). The level of ftn-1 expression was similar in the two strains after 6 h in 1% O2. These graphs represent the average of 3 biological repeats. (B) A schematic working model presenting the inhibitory function of hydroxylated HIF-1 (HIF-1-OH). The egl-9 mutation inhibits the formation of HIF-1-OH, and thus results in constitutive ftn-1 expression. By contrast, the vhl-1 mutation results in HIF-1-OH enrichment, and therefore constitutive inhibition of ftn-1 expression. (C) Bar graphs presenting the expression of ftn-1 at 21% O2 and after 6 h exposure in 1% O2 in wild-type (N2) worms and egl-9 and vhl-1 mutants (B) or in HIF-1(P621G) transgenic worms (D). In (C), asterisks indicate significance for comparisons with N2 animals at the beginning of the experiments (21% O2, time = 0). In (D), the comparison was against ftn-1- expression in N2 worms at 1% O2. These graphs represent the average of 3–4 biological repeats. Multiple t-tests with Holm-Sidak multiple comparison correction. Error bars represent SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001, ns = non-significant.