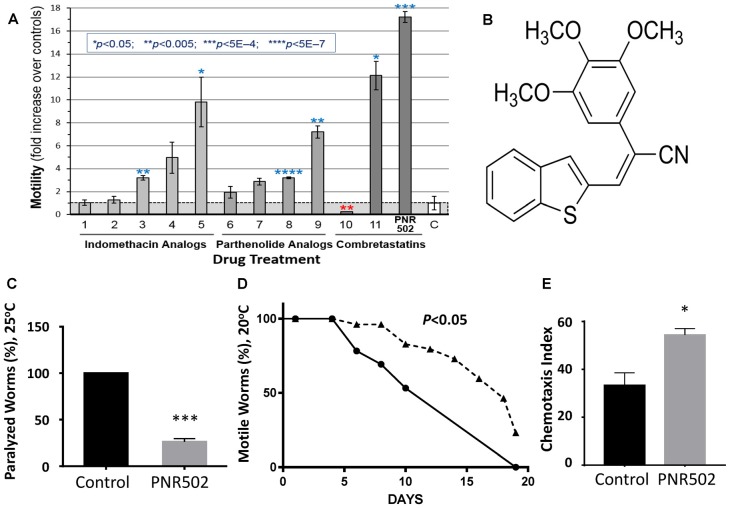
Figure 1.
PNR502 is exceptionally effective in reducing amyloid toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans). (A) Three families of drugs ameliorate a locomotion deficit in C. elegans (strain CL4176) expressing human Aβ1–42 in muscle. Worms were induced at the L4/adult transition, by upshift from 20° to 25.5°C, and then maintained for 41 h on solid media with the indicated compounds (at 10 μM) or vehicle. For motility assay, worms were placed 20 per well, in S basal medium in a flat-bottom 96-well plate. Movement was monitored with wMicrotracker (NemaMetrix), a motion-tracking device that records disruptions of 4 infrared beams per well. Error bars show standard deviations. Significance, in 2-tailed t tests, of difference between treated groups and controls (bar “C” at right): *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005; ***P < 5E-4; ****P < 5E-7. (B) The structure of PNR502. (C) The paralyzed fraction of CL4176 worms was reduced 75% by treatment with 10-μM PNR502 for 48 h after induction (as in A, assessed manually). (D) Uninduced CL4176 worms show progressive paralysis as they age at 20°C. The median time to paralysis is delayed 1.8-fold by continuous exposure to 10-μM PNR502. (E) CL2355 nematodes express human Aβ1–42 in all neurons, resulting in impaired chemotaxis 48 h after induction. Exposure to 5-μM PNR502 preserves chemotaxis relative to vehicle-only control worms. (C,E) Treated groups differ from controls by the Fisher exact test: *P < 0.01; ***P < 0.0001.