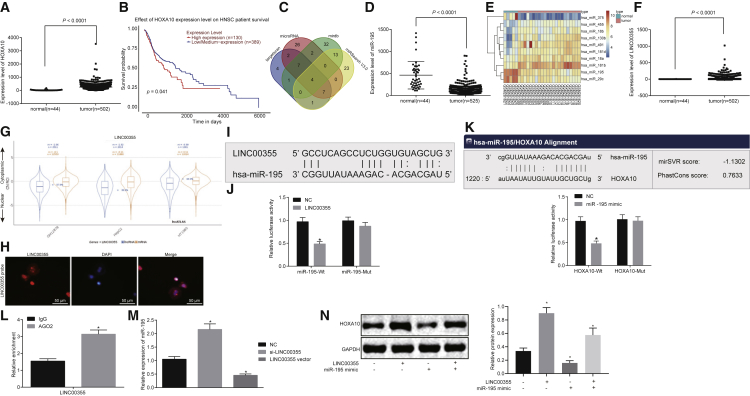
Figure 2.
LINC00355 Competitively Binds to miR-195 and LINC00355 Silencing Elevates the Expression of miR-195
(A) The expression of HOXA10 in the normal tissues and the HNSCC tissues retrieved from TCGA database. (B) The survival rate analysis with HOXA10 retrieved from TCGA database. (C) Prediction of target miRNAs of HOXA10. (D) Expression of miR-195 in the normal tissues and the HNSCC tissues retrieved from TCGA database. (E) The heatmap of the top 10 differentially expressed genes from the dataset of GSE11163 (human papillomavirus infection negative). (F) Expression of LINC00355 in the normal tissues and the HNSCC tissues retrieved from TCGA data. (G) Bioinformatics prediction of subcellular localization of LINC00355. (H) Subcellular location of LINC00355 detected by the FISH assay (200×). (I) Prediction of the bind site between LINC00355 and miR-195 in the website http://www.mircode.org/. (J) The relationship between LINC00355 and miR-195 verified by the dual luciferase reporter gene assay. (K) Predication of binding site between miR-195 and HOXA10. (L) The binding of LINC00355 to Ago2 protein detected by the RNA co-immunoprecipitation assay. (M) The expression of miR-195 determined by qRT-PCR. (N) The protein expression of HOXA10 in response to the altered expression of LINC00355 and miR-195 as measured by western blot analysis. The measurement data were expressed as mean ± SE. Data comparison between two groups was conducted using unpaired t test (J–L). Data among multiple groups were compared by one-way ANOVA (M and N). The experiment was repeated three times. In (J) and (M), *p < 0.05 versus the NC group; in (L), *p < 0.05 versus the IgG group. The T shape line indicates SD.