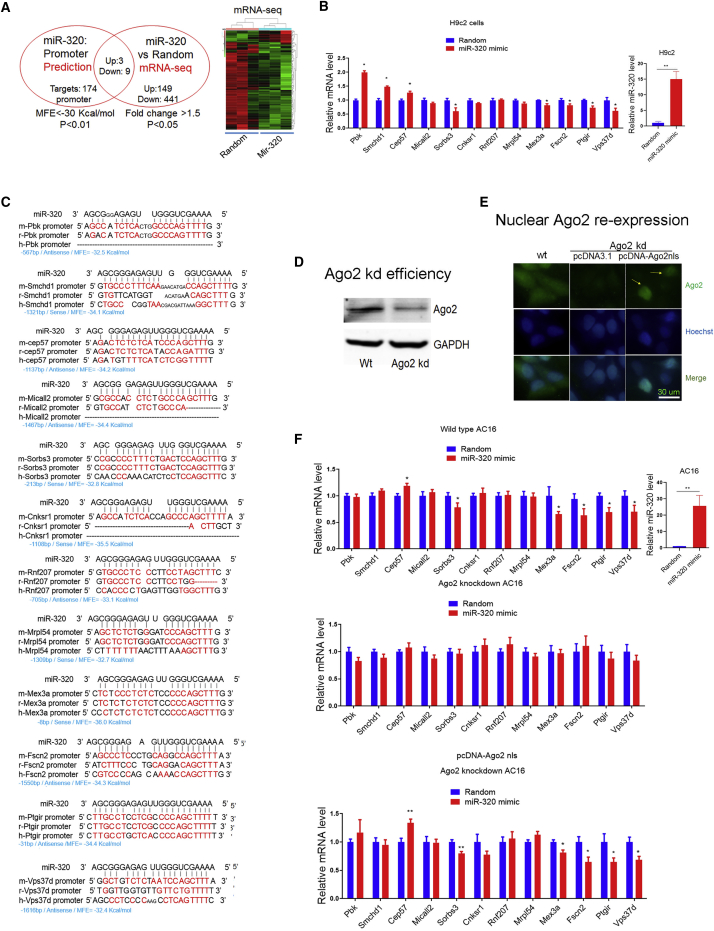
Figure 2.
Identification of miR-320 Targets in the Nucleus
(A) Strategy to identify miR-320 targets in the nucleus by using bioinformatics and mRNA-seq. Twelve targeting genes (up: Pbk, Smchd1, and Cep57; down: Micall2, Sorbs3, Cnksr1, Rnf207, Mrpl54, Mex3a, Fscn2, Ptgir, and Vps37d) were regulated by miR-320 in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. (B) qRT-PCR validation of genes regulated by miR-320; n = 3, *p < 0.05 versus random by t test. (C) Sequence alignment of miR-320 on gene promoter regions among species. (D) CRISPR-Cas9-mediated Ago2 kd in human AC16 cardiomyocytes. (E) Nuclear Ago2 re-expression in Ago2 kd AC16 cardiomyocytes. Scale bar: 30 μm. (F) Regulation of miR-320 on targeting genes in wild-type (WT), Ago2 kd, and nuclear Ago2 re-expression AC16 cells. qRT-PCR revealed that re-expression restored miR-320-mediated regulation on Cep57, Mex3a, Fscn2, Ptgir, and Vps37d; n = 8, *p < 0.05 versus random by t test.