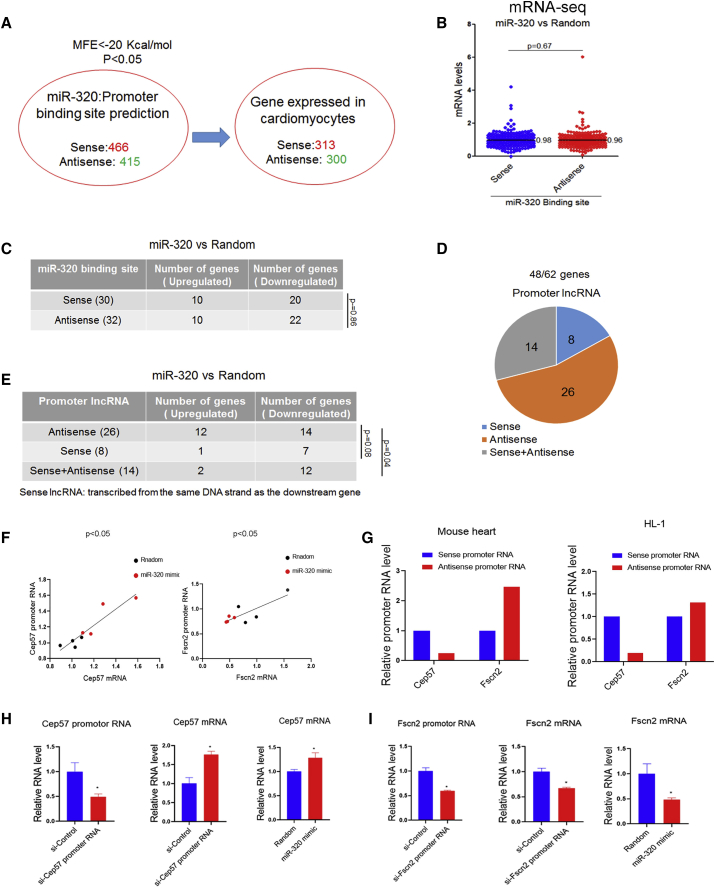
Figure 5.
The Activation/Inhibition Effects of miR-320 Were Likely ncRNA Dependent
(A) miR-320 binding strand analysis. With the use of the microPIR database, miR-320 was predicted to target 466 sense and 415 antisense promoters. (B) Regulation of miR-320 on sense-strand binding genes and antisense binding genes (all targeting genes). miR-320 binding on gene sense or antisense promoters had no differences in affecting gene expression. (C) Regulation of miR-320 on sense-strand binding genes and antisense binding genes (significantly regulated genes, with p < 0.05). (D) Promoter RNA classification for significantly regulated genes by miR-320. (E) Regulation of miR-320 on genes with sense or antisense promoter RNAs. (F) Coordinated expression of Cep57 and Fscn2 mRNA and their promoter RNAs was observed in HL-1 cells treated with miR-320. (G) Strand-specific qRT-PCR revealed a higher abundance of sense promoter RNA for Cep57 and antisense promoter RNA for Fscn2 in mice heart and HL-1 cell. (H) Cep57 promoter RNA-specific siRNA and miR-320 both increased Cep57 mRNA levels, as determined by qRT-PCR. (I) Fscn2 promoter RNA-specific siRNA and miR-320 both decreased Fscn2 mRNA levels, as determined by qRT-PCR; n = 3, *p < 0.05 versus random by t test.