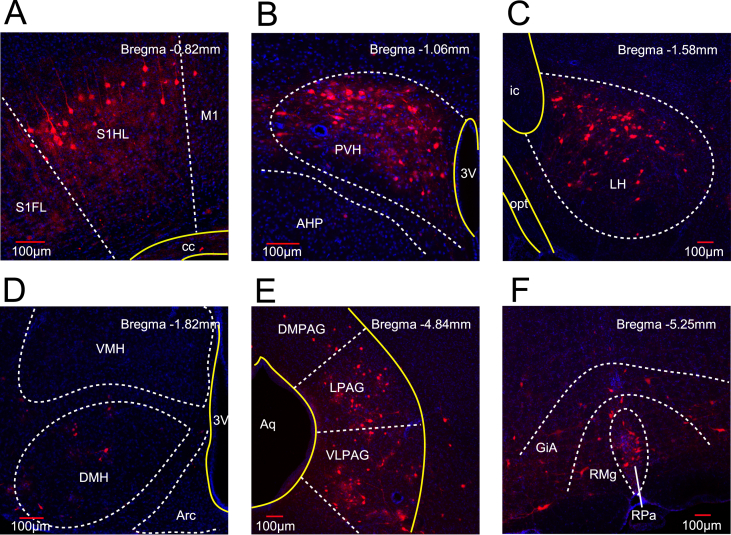
Figure 5.
BAT-connected neurons in mouse brain. (A–F) Immunostaining images showing BAT-connected neurons in six brain areas. PRV-614-mRFP, a transsynaptic retrograde tracer labeling neuronal circuits, was injected into the left BAT of mice. These mice were processed for immunostaining 6 days after PRV infection. Dashed lines (white) indicate the separation of the nucleus or subnucleus; solid lines (yellow) indicate neuronal fibers or brain ventricles. Scale bar (red), 100 μm. (A) Bregma −0.82 mm. PRV mRFP fluorescence was detected in S1HL (primary sensory cortex, hindlimb region). S1FL, primary sensory cortex, forelimb region; M1, primary motor cortex; cc, corpus callosum. (B) Bregma −1.06 mm. PRV fluorescence was expressed in the PVH (paraventricular hypothalamus). AHP, anterior hypothalamic area, posterior part; 3V, the third ventricle. (C) Bregma −1.58 mm. PRV fluorescence was expressed in LH. opt, optic tract; ic, internal capsule. (D) Bregma −1.82 mm. A few PRV + neurons were detected in the VMH. DMH, dorsal medial hypothalamus; Arc, arcuate hypothalamic nucleus. (E) Bregma −4.84 mm eGFP fluorescence was expressed in the PAG (periaqueductal gray), mainly including the lateral part (LPAG) and dorsolateral part (DLPAG). A few PRV + neurons were detected in the DMPAG (dorsomedial part PAG). Aq, aqueduct. (F) Bregma −5.25 mm. PRV fluorescence was expressed in RPa (raphe pallidus nucleus), RMg (raphe magnus nucleus), and GiA (gigantocellular reticular nucleus, alpha part).