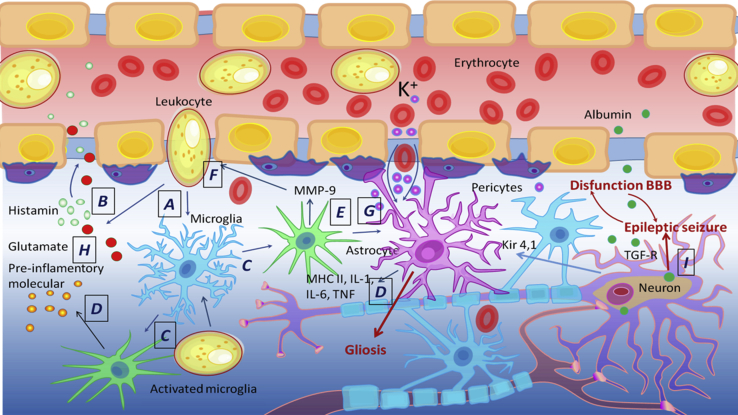
Figure 2.
Blood-Brain Barrier in Epilepsy
(A–F) Disruption of the BBB induces blood cells to enter the brain (A); leukocytes cause inflammation, secrete histamine (B), and activate microglia and astrocytes (C); activated microglia and astrocytes increase inflammation (D), activate metalloproteinase MMP-9 (E), and increase the BBB permeability (F). (G and H) Disruption increases the content of intracellular potassium (G) and glutamate (H) ions. (I) Disruption increases the entry of albumin into the brain, absorbed by neurons and astrocytes through TGF-β receptors, as a result of which Kir 4.1 permeability of potassium channels in astrocytes is reduced. Systemic inflammatory disorders cause an accumulation of inflammatory mediators and contribute to the destruction of the BBB. All processes together increase the excitability of neurons and stimulate epileptimorphic seizures, and the excessive activation of astrocytes stimulates gliosis.