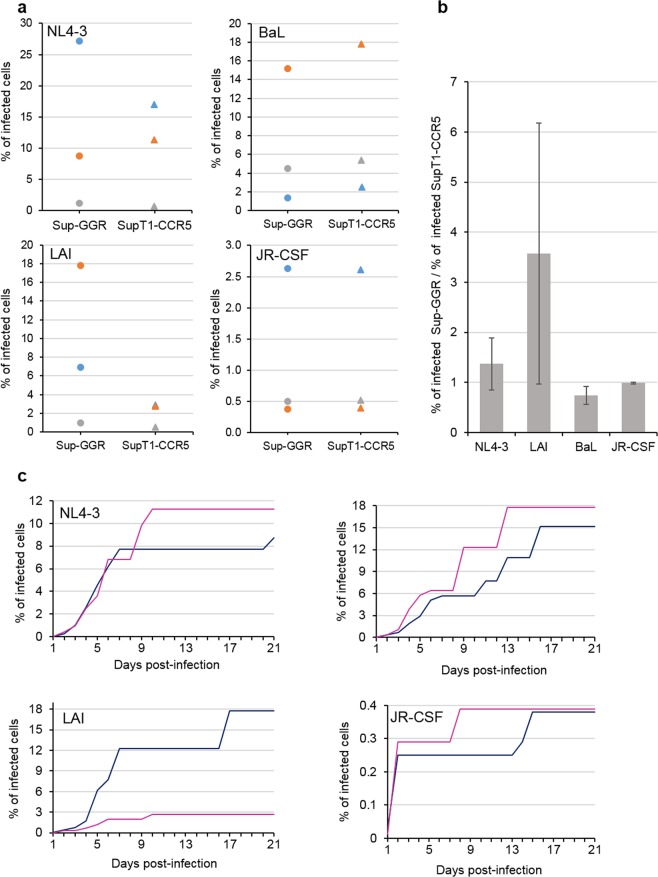
Figure 2.
Sup-GGR can readily detect X4-tropic viruses (NL4-3 and LAI) or R5-tropic viruses (BaL and JR.CSF). (a) SupT1-CCR5 cells were infected with various strains of viruses (NL4-3, LAI, BaL or JR-CSF) and serial fivefold dilution (starting from 625 cells per well) of infected cells were co-cultured with uninfected Sup-GGR (circle) or SupT1-CCR5 (triangle) in 96 well plates, with 10 wells/dilution. Cytopathic effects were assessed every day for 21 days and the percentage of infected cells in the stock was calculated based on limiting dilution statistics. Three independent experiments are represented, each experiment is depicted by a different color (blue, grey or orange). (b) Ratio of the percentage of infected cells in the stock detected by Sup-GGR over that detected by SupT1-CCR5 for each strain of virus, using data from (a). Three independent experiments were performed. Error bars indicates standard deviation. The ratios are around 1 for all four strains of viruses indicating that SupGGR is at least as efficient as SupT1-CCR5 in supporting HIV replication. (c) Percentage of infected cells as determined for Sup-GGR (blue) or SupT1-CCR5 (pink) at different days post-infection demonstrating the kinetics of infection. One representative experiment from 3 replicates is presented.