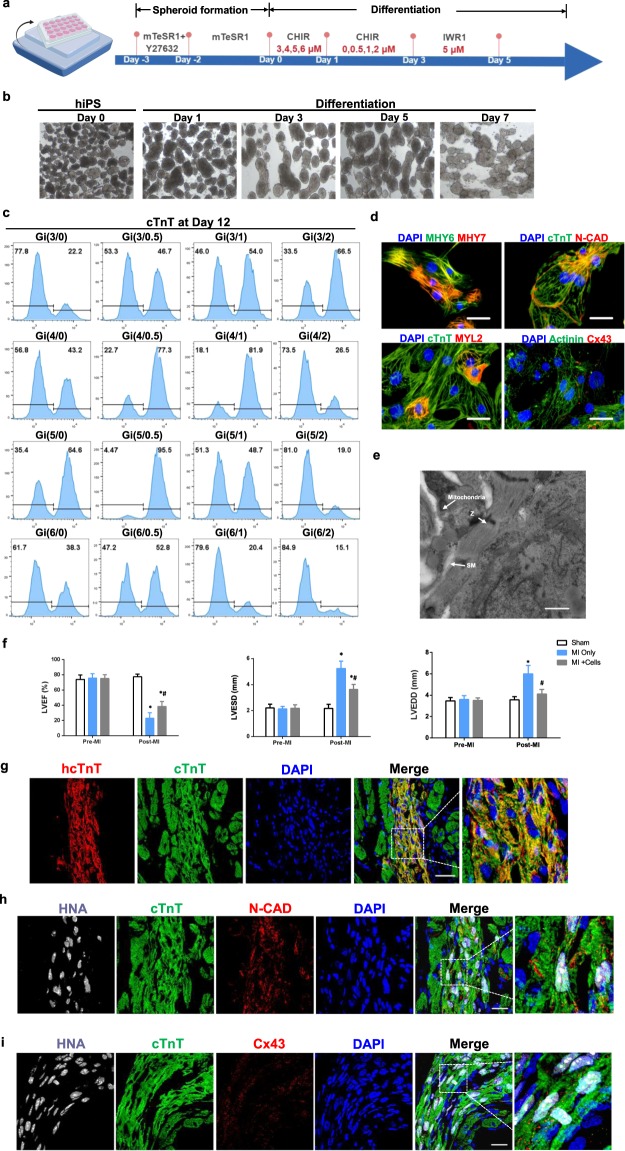
Figure 5.
The Gi(I/M)Wi protocol can be adapted to efficiently induce hiPSC-CM differentiation in suspended cells. (a) Application of the Gi(I/M)Wi protocol to a cell-suspension system is illustrated schematically. The hiPSCs were allowed to form spheroids for 3 days before differentiation was initiated on Day 0, and 16 combinations of CHIR initiation (3, 4, 5, or 6 μM) and maintenance (0, 0.5, 1, or 2 μM) doses were evaluated. (b) Representative bright-field images of differentiating spheroids at the indicated time points. (c–e) Twelve days after differentiation was initiated (c) cTnT expression was evaluated in cells from all 16 Gi(I/M)Wi treatment groups via flow cytometry (n = 3 different batches of differentiated cells); and (d,e) cells from the Gi(5/0.5) group were (d) immunofluorescently stained for the expression of MYH6, MYH7, cTnT, N-cadherin (N-CAD), MYL2, α-actinin (Actinin) and Cx43 (bars = 40 μm), and (e) imaged via transmission electron microscopy (Z: Z-band, SM: sarcomere; bars = 2 μm). (f,g) Myocardial infarction (MI) was surgically induced in mice; then, the animals were administered 1 million hiPSC-CMs (MI + Cells) or 25 μl of PBS (MI Only). The hiPSC-CMs had been differentiated via the Gi(I/M)Wi protocol in a cell-suspension system, and a third group of animals (the Sham group) underwent sham surgery and recovered without either experimental treatment. (f) Cardiac function was evaluated via echocardiographic assessments of LVEF, LVESD, and LVEDD before MI and 30 days afterward. N = 7 in sham and MI only group. N = 8 in MI + cells group. *P < 0.05 vs Sham, #P < 0.05 vs MI only. (g–i) Heart tissues were harvested from MI + Cells animals 30 days after MI and immunofluorescently stained for the expression of (g) human cTnT (hcTnT), cTnT; (h) HNA, cTnT and N-CAD; (i) HNA, cTnT and Cx43; nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (bars = 20 μm).