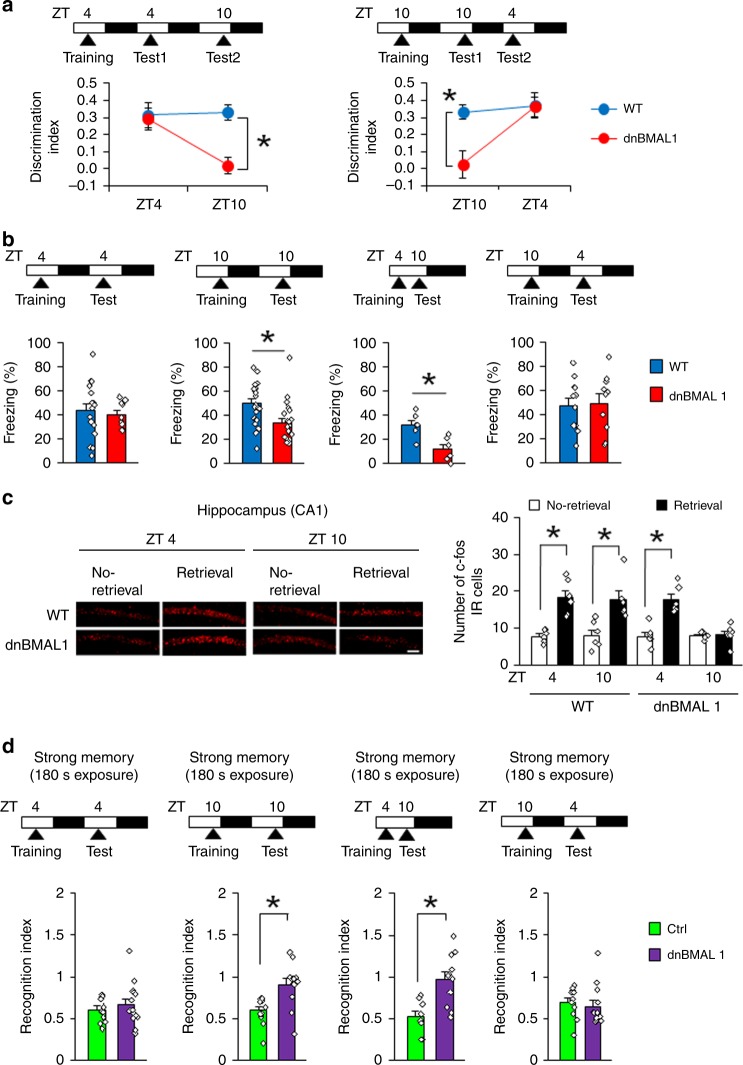
Fig. 4. Memory retrieval deficits in dnBMAL1 mice generalize to hippocampus-dependent memory.
a, b Experimental designs are illustrated at the top of each panel. Memory retrieval is impaired at ZT10 in dnBMAL1 mice for a novel object recognition task and b contextual fear memory. c Consistent with impaired memory retrieval at ZT10, dnBMAL1 mice show reduced c-fos expression in CA1 region of hippocampus after retrieval of contextual fear memory. (Left panels) Representative images of c-fos immunohistochemistry. Scale bar, 100 μm. (Right panel) Quantification of the number of c-fos immunoreactive (IR) cells. d dnBMAL1 expression in the hippocampus impairs retrieval of social recognition memory at ZT10 but not at ZT4 (Recognition index). Experimental designs are illustrated at the top of each panel. One-way ANOVAs with group reveal significant effect of dnBMAL1 when dnBMAL1 group is tested at ZT10 but not at ZT4. Ctrl control. All values are mean ± SEM. Individual data points are displayed as dots. *p < 0.05 as determined by three-way (c), two-way (a), or one-way (b, d) ANOVA with post hoc test. The results of the statistical analyses are presented in Supplementary Table 2. Source data are provided as a source data file.