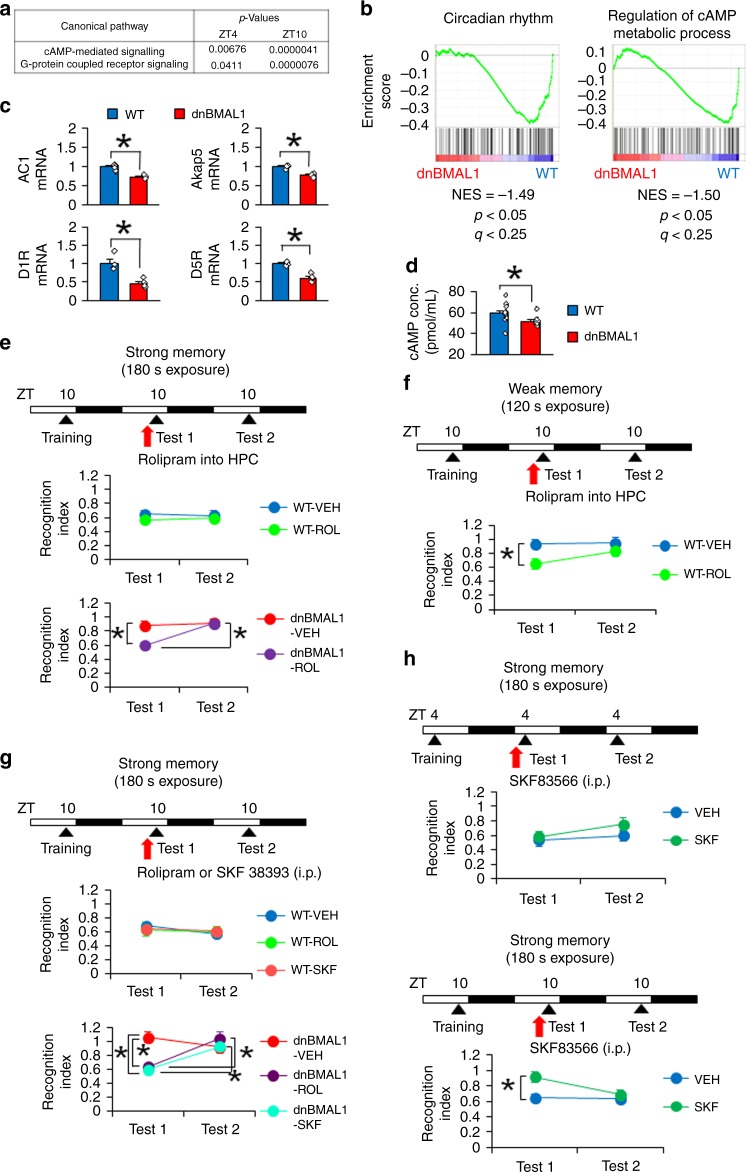
Fig. 5. Impaired Dopamine D1/5R-cAMP signal and its pharmacological rescues of memory retrieval deficits.
a Changes in cAMP-mediated signaling and G-protein coupled receptor signaling in the hippocampus of dnBMAL1 mice (ingenuity pathway analysis). b Downregulation of gene set for circadian rhythm (left) and regulation of cAMP metabolic process (right) in the hippocampus of dnBMAL1 mice at ZT10 (Enrichment plot). NES normalized enrichment score. a, b All groups (n = 3). c, d Reduced AC1, AKAP5, D1R, and D5R mRNAs (c) and cAMP (d) levels in the hippocampus of dnBMAL1 mice at ZT10. The graph represents fold changes compared to the expression levels in WT (c). e–h Experimental designs at the top of each panel. Retrieval is tested twice (Tests 1 and 2) at ZT10 following strong (e, g, h) or weak (f) training at ZT10. Dorsal hippocampal micro-infusion (e, f) or systemic injection (g, h) of drug at 30 min before Test 1. Rescues of impaired retrieval by hippocampal rolipram in dnBMAL1 (e, strong training) and WT mice (f, weak training) and by systemic SKF38393 (D1/5R agonist) or rolipram injection at Test 1 in dnBMAL1 mice (g). Impaired retrieval by systemic SKF83566 injection (D1/5R antagonist) in WT mice (h, Supplementary Fig. 5). HPC hippocampus, VEH vehicle. All values are mean ± SEM. Individual data points are displayed as dots. *p < 0.05 as determined by three-way (e, g), two-way (f, h), or one-way (c, d) ANOVA with post hoc test. The results of the statistical analyses are presented in Supplementary Table 2. Source data are provided as a source data file.