Figure 5.
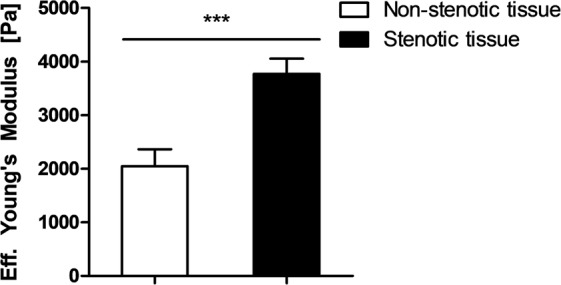
Tissue stiffness of stenotic intestinal tissue was significantly elevated compared to non-stenotic intestinal tissue of Crohn’s disease patients. Using a cantilever-based nanointender (Piuma Nanoindenter by Optics11, Amsterdam, N.L.), the Young’s Modulus of cryostat sections of non-stenotic and stenotic segments of the intestinal wall were assessed. Performing 139 measurements (n = 44 in non-stenotic tissue and n = 95 in stenotic tissue), stenotic tissue had a significant higher stiffness compared to non-stenotic tissue (p < 0.001). Pa = Pascal. Data are mean ± standard error of mean (SEM). Statistical analysis was performed using Mann-Whitney U test. Two-sided p values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
